Comparison of the vasodilatory effects of sodium nitroprusside vs. nitroglycerin
- PMID: 28572495
- PMCID: PMC5583612
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00167.2017
Comparison of the vasodilatory effects of sodium nitroprusside vs. nitroglycerin
Abstract
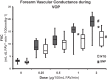
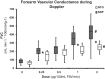
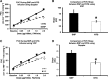
The vasodilatory mechanism of Nntroglycerin (NTG) is similar to sodium nitroprusside (SNP) in regard to action on guanosine 3'5'-monophosphate (cyclic GMP) via nitric oxide. However, it is unknown whether NTG can achieve the same magnitude of vasodilation in the forearm as SNP. Therefore, the purpose of the study was to evaluate the differences in forearm blood flow (FBF) and forearm vascular conductance (FVC) during escalating infusions of NTG vs. SNP at similar concentration doses and rates. We measured FBF using venous occlusion plethysmography (VOP) and Doppler ultrasound in eight young, healthy participants (mean age = 28 ± 2 yr) during four forearm volume (FAV)-specific doses (0.25, 0.5, 1, and 2 µg·100 ml FAV-1·min-1) of SNP and NTG infused via a brachial artery catheter. There was a significant difference in FVC of SNP vs. NTG only at the higher doses, as measured by VOP (14.9 ± 1.4 and 18.3 ± 1.5 vs. 11.6 ± 1.2 and 12.5 ± 1.2 ml/dl FAV-1·min-1·100 mmHg-1). FVC as measured by Doppler ultrasound unadjusted for FAV was significantly different at the lowest and the higher two doses of SNP compared with NTG (202.1 ± 25.8, 329.4 ± 46.7, and 408 ± 63.5 vs. 142.9 ± 22.4, 217.2 ± 18.8, and 247.5 ± 18.2 ml·min-1·100 mmHg-1). SNP induces significantly higher vasodilatory actions compared with NTG. However, NTG is comparable in eliciting equivalent vasodilator effects to SNP during low concentration doses when measured by VOP. Importantly, for forearm pharmacology studies, NTG can elicit marked endothelium-independent forearm vasodilation.NEW & NOTEWORTHY We compared the vasodilatory capacities of NTG vs. SNP at similar concentration doses and rates into the forearm. Based on the results of the study, it may be feasible to use intra-arterial NTG as a measure of endothelial-independent vasodilator in research studies. However, NTG dosing may need to be higher if used as an endothelial-independent vasodilator due to significant differences in the vasodilatory effects during higher doses of SNP compared with NTG.
Keywords: Doppler ultrasound; vasodilators; venous occlusion plethysmography.
Copyright © 2017 the American Physiological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enhancement of endothelium-dependent vasodilation by low-dose nitroglycerin in patients with congestive heart failure.Circulation. 1994 Apr;89(4):1609-14. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.89.4.1609. Circulation. 1994. PMID: 8149528
-
Sex differences in salt sensitivity to nitric oxide dependent vasodilation in healthy young adults.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2012 Mar;112(6):1049-53. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01197.2011. Epub 2011 Dec 22. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2012. PMID: 22194324 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of endothelium-dependent vasodilation in the human peripheral circulation.Clin Physiol. 2000 Nov;20(6):440-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2281.2000.00281.x. Clin Physiol. 2000. PMID: 11100391 Clinical Trial.
-
Venous occlusion plethysmography in cardiovascular research: methodology and clinical applications.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2001 Dec;52(6):631-46. doi: 10.1046/j.0306-5251.2001.01495.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11736874 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Nitric oxide and vascular reactivity in African American patients with hypertension.J Card Fail. 2003 Oct;9(5 Suppl Nitric Oxide):S199-204; discussion S205-9. doi: 10.1054/s1071-9164(03)00588-8. J Card Fail. 2003. PMID: 14583889 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Sodium nitroprusside protects HFD induced gut dysfunction via activating AMPKα/SIRT1 signaling.BMC Gastroenterol. 2021 Oct 2;21(1):359. doi: 10.1186/s12876-021-01934-y. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 34600475 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Exercise on Vascular Function in Middle-Aged and Older Adults: A Scoping Review.Sports (Basel). 2022 Dec 14;10(12):208. doi: 10.3390/sports10120208. Sports (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36548505 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of resistance vessel function in human skeletal muscle: guidelines for experimental design, Doppler ultrasound, and pharmacology.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2020 Feb 1;318(2):H301-H325. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00649.2019. Epub 2019 Dec 30. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31886718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sodium Nitroprusside-Enhanced Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Improves Blood Flow by Pulmonary Vasodilation Leading to Higher Oxygen Requirements.JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2020 Feb 5;5(2):183-192. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2019.11.010. eCollection 2020 Feb. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2020. PMID: 32140624 Free PMC article.
-
A Unification of Nanotopography and Extracellular Matrix in Electrospun Scaffolds for Bioengineered Hepatic Models.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2023 Jun 19;6(6):2158-2171. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.3c00032. Epub 2023 Jun 7. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2023. PMID: 37283498 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eisenach JH, Schroeder DR, Pike TL, Johnson CP, Schrage WG, Snyder EM, Johnson BD, Garovic VD, Turner ST, Joyner MJ. Dietary sodium restriction and beta2-adrenergic receptor polymorphism modulate cardiovascular function in humans. J Physiol 574: 955–965, 2006. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2006.112102. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Friederich JA, Butterworth JF 4th. Sodium nitroprusside: twenty years and counting. Anesth Analg 81: 152–162, 1995. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

