Deletion of interleukin 1 receptor-associated kinase 1 (Irak1) improves glucose tolerance primarily by increasing insulin sensitivity in skeletal muscle
- PMID: 28572512
- PMCID: PMC5519380
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M117.779108
Deletion of interleukin 1 receptor-associated kinase 1 (Irak1) improves glucose tolerance primarily by increasing insulin sensitivity in skeletal muscle
Abstract
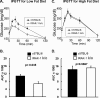
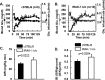
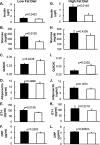
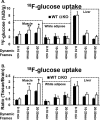
Chronic inflammation may contribute to insulin resistance via molecular cross-talk between pathways for pro-inflammatory and insulin signaling. Interleukin 1 receptor-associated kinase 1 (IRAK-1) mediates pro-inflammatory signaling via IL-1 receptor/Toll-like receptors, which may contribute to insulin resistance, but this hypothesis is untested. Here, we used male Irak1 null (k/o) mice to investigate the metabolic role of IRAK-1. C57BL/6 wild-type (WT) and k/o mice had comparable body weights on low-fat and high-fat diets (LFD and HFD, respectively). After 12 weeks on LFD (but not HFD), k/o mice (versus WT) had substantially improved glucose tolerance (assessed by the intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test (IPGTT)). As assessed with the hyperinsulinemic euglycemic glucose clamp technique, insulin sensitivity was 30% higher in the Irak1 k/o mice on chow diet, but the Irak1 deletion did not affect IPGTT outcomes in mice on HFD, suggesting that the deletion did not overcome the impact of obesity on glucose tolerance. Moreover, insulin-stimulated glucose-disposal rates were higher in the k/o mice, but we detected no significant difference in hepatic glucose production rates (± insulin infusion). Positron emission/computed tomography scans indicated higher insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in muscle, but not liver, in Irak1 k/o mice in vivo Moreover, insulin-stimulated phosphorylation of Akt was higher in muscle, but not in liver, from Irak1 k/o mice ex vivo In conclusion, Irak1 deletion improved muscle insulin sensitivity, with the effect being most apparent in LFD mice.
Keywords: Akt PKB; IRAK-1; glucose tolerance; inflammation; insulin resistance; metabolism; muscle.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health or reflect the position or policy of the Department of Veterans Affairs or the United States government
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rac1 muscle knockout exacerbates the detrimental effect of high-fat diet on insulin-stimulated muscle glucose uptake independently of Akt.J Physiol. 2018 Jun;596(12):2283-2299. doi: 10.1113/JP275602. Epub 2018 May 10. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29749029 Free PMC article.
-
Skeletal muscle-specific overexpression of heat shock protein 72 improves skeletal muscle insulin-stimulated glucose uptake but does not alter whole body metabolism.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018 Aug;20(8):1928-1936. doi: 10.1111/dom.13319. Epub 2018 May 3. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018. PMID: 29652108
-
Pancreastatin inhibitor PSTi8 protects the obesity associated skeletal muscle insulin resistance in diet induced streptozotocin-treated diabetic mice.Eur J Pharmacol. 2020 Aug 15;881:173204. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173204. Epub 2020 May 19. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32439261
-
Recent Advances in IRAK1: Pharmacological and Therapeutic Aspects.Molecules. 2024 May 9;29(10):2226. doi: 10.3390/molecules29102226. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38792088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IRAK1 and IRAK4 as emerging therapeutic targets in hematologic malignancies.Curr Opin Hematol. 2022 Jan 1;29(1):8-19. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0000000000000693. Curr Opin Hematol. 2022. PMID: 34743084 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4/Midline-1 Axis Promotes T Lymphocyte Motility in Atherosclerosis.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Mar;10(9):e2204194. doi: 10.1002/advs.202204194. Epub 2023 Jan 22. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 36683148 Free PMC article.
-
Graph Embedding Based Novel Gene Discovery Associated With Diabetes Mellitus.Front Genet. 2021 Nov 25;12:779186. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.779186. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34899863 Free PMC article.
-
Non-digestive stachyose enhances bioavailability of isoflavones for improving hyperlipidemia and hyperglycemia in mice fed with high fat diet.J Food Drug Anal. 2021 Mar 15;29(1):87-97. doi: 10.38212/2224-6614.3078. J Food Drug Anal. 2021. PMID: 35696221 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in plasma IRAK-M in patients with prediabetes and its relationship with related metabolic indexes: a cross-sectional study.J Int Med Res. 2022 Aug;50(8):3000605221111275. doi: 10.1177/03000605221111275. J Int Med Res. 2022. PMID: 36039603 Free PMC article.
-
IL-1 induces mitochondrial translocation of IRAK2 to suppress oxidative metabolism in adipocytes.Nat Immunol. 2020 Oct;21(10):1219-1231. doi: 10.1038/s41590-020-0750-1. Epub 2020 Aug 10. Nat Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32778760 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Muniyappa R., Lee S., Chen H., and Quon M. J. (2008) Current approaches for assessing insulin sensitivity and resistance in vivo: Advantages, limitations, and appropriate usage. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 294, E15–E26 - PubMed
-
- Kahn C. R. (1994) Banting Lecture. Insulin action, diabetogenes, and the cause of type II diabetes. Diabetes 43, 1066–1084 - PubMed
-
- Kim Y.-B., Kotani K., Ciaraldi T. P., Henry R. R., and Kahn B. B. (2003) Insulin-stimulated protein kinase C λ/ζ activity is reduced in skeletal muscle of humans with obesity and type 2 diabetes: reversal with weight reduction. Diabetes 52, 1935–1942 - PubMed
-
- Matsumoto M., Pocai A., Rossetti L., Depinho R. A., and Accili D. (2007) Impaired regulation of hepatic glucose production in mice lacking the forkhead transcription factor Foxo1 in liver. Cell Metab. 6, 208–216 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

