Ergosterol isolated from the basidiomycete Pleurotus salmoneostramineus affects Trypanosoma cruzi plasma membrane and mitochondria
- PMID: 28572816
- PMCID: PMC5450401
- DOI: 10.1186/s40409-017-0120-0
Ergosterol isolated from the basidiomycete Pleurotus salmoneostramineus affects Trypanosoma cruzi plasma membrane and mitochondria
Abstract
Background: Major drawbacks of the available treatment against Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis) include its toxicity and therapeutic inefficiency in the chronic phase of the infection, which makes it a concern among neglected diseases. Therefore, the discovery of alternative drugs for treating chronic Chagas disease requires immediate action. In this work, we evaluated the mushroom Pleurotus salmoneostramineus in the search for potential antiparasitic compounds.
Methods: Fruit bodies of the basidiomycete Pleurotus salmoneostramineus were triturated and submitted to organic solvent extraction. After liquid-liquid partition of the crude extract, three fractions were obtained and the bioguided fractionation study was conducted to isolate the active metabolites. The elucidation of the chemical structure was performed using GC-MS and NMR techniques. The biological assays for antiparasitic activity were carried out using trypomastigotes of Trypanosoma cruzi and murine macrophages for mammalian cytotoxicity. The mechanism of action of the isolated compound used different fluorescent probes to evaluate the plasma membrane permeability, the potential of the mitochondrial membrane and the intracellular levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS).
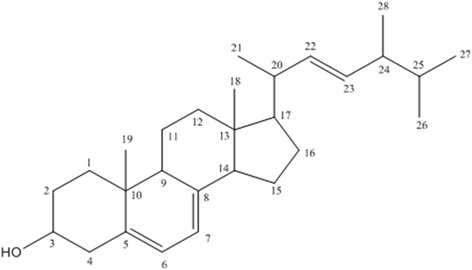
Results: The most abundant fraction showing the antiparasitic activity was isolated and chemically elucidated, confirming the presence of ergosterol. It showed anti-Trypanosoma cruzi activity against trypomastigotes, with an IC50 value of 51.3 μg/mL. The compound demonstrated no cytotoxicity against mammalian cells to the maximal tested concentration of 200 μg/mL. The mechanism of action of ergosterol in Trypanosoma cruzi trypomastigotes resulted in permeabilization of the plasma membrane, as well as depolarization of mitochondrial membrane potential, leading to parasite death. Nevertheless, no increase in ROS levels could be observed, suggesting damages to plasma membrane rather than an induction of oxidative stress in the parasite.
Conclusions: The selection of naturally antiparasitic secondary metabolites in basidiomycetes, such as ergosterol, may provide potential scaffolds for drug design studies against neglected diseases.
Keywords: Ergosterol; Mechanism of action; Pleurotus salmoneostramineus; Trypanosoma cruzi.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Antiparasitic activity and effect of casearins isolated from Casearia sylvestris on Leishmania and Trypanosoma cruzi plasma membrane.Phytomedicine. 2014 Apr 15;21(5):676-81. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2014.01.004. Epub 2014 Feb 18. Phytomedicine. 2014. PMID: 24560122
-
(-)-T-Cadinol-a Sesquiterpene Isolated From Casearia sylvestris (Salicaceae)-Displayed In Vitro Activity and Causes Hyperpolarization of the Membrane Potential of Trypanosoma cruzi.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 3;12:734127. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.734127. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34803682 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial peptides isolated from Phyllomedusa nordestina (Amphibia) alter the permeability of plasma membrane of Leishmania and Trypanosoma cruzi.Exp Parasitol. 2013 Dec;135(4):655-60. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2013.09.016. Epub 2013 Oct 8. Exp Parasitol. 2013. PMID: 24113627
-
Experimental models in Chagas disease: a review of the methodologies applied for screening compounds against Trypanosoma cruzi.Parasitol Res. 2018 Nov;117(11):3367-3380. doi: 10.1007/s00436-018-6084-3. Epub 2018 Sep 19. Parasitol Res. 2018. PMID: 30232605 Review.
-
Metallomics: An Essential Tool for the Study of Potential Antiparasitic Metallodrugs.ACS Omega. 2024 Mar 25;9(14):15744-15752. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c10200. eCollection 2024 Apr 9. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38617611 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Potential Beneficial Effects and Pharmacological Properties of Ergosterol, a Common Bioactive Compound in Edible Mushrooms.Foods. 2023 Jun 29;12(13):2529. doi: 10.3390/foods12132529. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37444267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alterations in Mycelial Morphology and Flow Cytometry Assessment of Membrane Integrity of Ganoderma boninense Stressed by Phenolic Compounds.Biology (Basel). 2021 Sep 18;10(9):930. doi: 10.3390/biology10090930. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34571807 Free PMC article.
-
Enyne acetogenins from Porcelia macrocarpa displayed anti-Trypanosoma cruzi activity and cause a reduction in the intracellular calcium level.Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 24;13(1):10254. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-37520-3. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37355735 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial activities of metabolites isolated from endophytic Aspergillus flavus of Sarcophyton ehrenbergi supported by in-silico study and NMR spectroscopy.Fungal Biol Biotechnol. 2023 Aug 2;10(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s40694-023-00161-2. Fungal Biol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37533082 Free PMC article.
-
MAT1-1 and MAT1-2 Ophiocordyceps xuefengensis and Comparison of Their Chemical Composition.Biology (Basel). 2024 Sep 2;13(9):686. doi: 10.3390/biology13090686. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39336113 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO. World Health Organization. Chagas disease. http://www.who.int/chagas/en/. Accessed 14 Jan 2017.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

