Primary elbow arthroplasty: problems and solutions
- PMID: 28572852
- PMCID: PMC5441620
- DOI: 10.1177/1758573216677200
Primary elbow arthroplasty: problems and solutions
Abstract
Prosthetic replacement of the elbow joint has continued to improve over time. Widespread implantation of certain designs has led to identification a few successful elements of elbow arthroplasty, as well as several opportunities for improvement. Current hot topics in elbow arthroplasty include triceps-preserving exposures, implantation of components with better-expected wear performance, management of the ulnar nerve, prevention of infection, and the development of successful cementless components. Total elbow arthroplasty has the potential to improve pain, function and quality of life for many patients with articular destruction secondary to inflammatory arthropathy or as a consequence of trauma. Continued advances in this field are key to make this operation as reliable and lasting as hip or knee arthroplasty.
Keywords: arthroplasty; elbow; surgical advances.
Figures
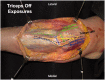
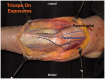

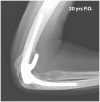

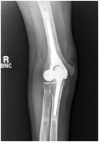

Similar articles
-
Modes of wear after semiconstrained total elbow arthroplasty.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008 Mar;90(3):609-19. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.F.01286. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008. PMID: 18310712
-
Allograft-prosthetic composite reconstruction for massive bone loss including catastrophic failure in total elbow arthroplasty.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013 Jun 19;95(12):1117-24. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.L.00747. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013. PMID: 23783209
-
The surgical treatment of periprosthetic elbow fractures around the ulnar stem following semiconstrained total elbow arthroplasty.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011 Aug 3;93(15):1399-407. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.J.00102. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011. PMID: 21915545
-
Elbow arthroplasty: where are we today? A narrative review.Acta Chir Belg. 2016 Apr;116(2):73-80. doi: 10.1080/00015458.2016.1147246. Acta Chir Belg. 2016. PMID: 27385293 Review.
-
Elbow arthroplasty using a convertible implant.Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg. 2005 Sep;9(3):153-63. doi: 10.1097/01.bth.0000181293.38237.f0. Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg. 2005. PMID: 16175119 Review.
Cited by
-
Failure of the linkage mechanism in a semi-constrained total elbow arthroplasty is a rare and unpredictable event: a review of seven cases.Int Orthop. 2024 Feb;48(2):537-545. doi: 10.1007/s00264-023-06015-1. Epub 2023 Oct 28. Int Orthop. 2024. PMID: 37897544 Review.
-
Descriptive analysis of total elbow arthroplasty for distal humerus fractures: 30-day complications.Clin Shoulder Elb. 2025 Mar;28(1):9-14. doi: 10.5397/cise.2024.00500. Epub 2024 Nov 19. Clin Shoulder Elb. 2025. PMID: 39558568 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted next generation sequencing for elbow periprosthetic joint infection diagnosis.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2021 Oct;101(2):115448. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2021.115448. Epub 2021 Jun 5. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34224945 Free PMC article.
-
Primary Linked Total Elbow Arthroplasty for Acute Distal Humerus Fracture Management: A Systematic Review of Clinical Outcome.Clin Orthop Surg. 2020 Dec;12(4):503-513. doi: 10.4055/cios20012. Epub 2020 Jul 21. Clin Orthop Surg. 2020. PMID: 33274028 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating proximal ulnar morphology in relation to the humeral flexion-extension axis.JSES Int. 2024 Nov 27;9(2):574-579. doi: 10.1016/j.jseint.2024.10.016. eCollection 2025 Mar. JSES Int. 2024. PMID: 40182270 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Voloshin I, Schippert DW, Kakar S, Kaye EK, Morrey BF. Complications of total elbow replacement: a systematic review. J Shoulder Elbow Surg Am 2011; 20: 158–168. - PubMed
-
- Thomopoulos S, Williams GR, Soslowsky LJ. Tendon to bone healing: differences in biomechanical, structural, and compositional properties due to a range of activity levels. J Biomech Engineering 2003; 125: 106–113. - PubMed
-
- Alonso-Llames M. Bilaterotricipital approach to the elbow. Its application in the osteosynthesis of supracondylar fractures of the humerus in children. Acta Orthoped Scand 1972; 43: 479–490. - PubMed
-
- Morrey BF, Adams RA. Semiconstrained elbow replacement for distal humeral nonunion. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1995; 77: 67–72. - PubMed
-
- Harmer LS, Sanchez-Sotelo J. Total elbow arthroplasty for distal humerus fractures. Hand Clin 2015; 31: 605–614. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
