Impact of creatinine methodology on glomerular filtration rate estimation in diabetes
- PMID: 28572883
- PMCID: PMC5437620
- DOI: 10.4239/wjd.v8.i5.222
Impact of creatinine methodology on glomerular filtration rate estimation in diabetes
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the influence of creatinine methodology on the performance of chronic kidney disease (CKD)-Epidemiology Collaboration Group-calculated estimated glomerular filtration rate (CKD-EPI-eGFR) for CKD diagnosis/staging in a large cohort of diabetic patients.
Methods: Fasting blood samples were taken from diabetic patients attending our clinic for their regular annual examination, including laboratory measurement of serum creatinine and eGFR.
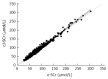
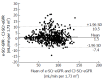
Results: Our results indicated an overall excellent agreement in CKD staging (kappa = 0.918) between the Jaffé serum creatinine- and enzymatic serum creatinine-based CKD-EPI-eGFR, with 9% of discordant cases. As compared to the enzymatic creatinine, the majority of discordances (8%) were positive, i.e., associated with the more advanced CKD stage re-classification, whereas only 1% of cases were negatively discordant if Jaffé creatinine was used for eGFR calculation. A minor proportion of the discordant cases (3.5%) were re-classified into clinically relevant CKD stage indicating mildly to moderately decreased kidney function (< 60 mL/min per 1.73 m2). Significant acute and chronic hyperglycaemia, assessed as plasma glucose and HbA1c levels far above the recommended glycaemic goals, was associated with positively discordant cases. Due to a very low frequency, positive discordance is not likely to present a great burden for the health-care providers, while intensified medical care may actually be beneficial for the small number of discordant patients. On the other hand, a very low proportion of negatively discordant cases (1%) at the 60 mL/min per 1.73 m2 eGFR level indicate a negligible possibility to miss the CKD diagnosis, which could be the most prominent clinical problem affecting patient care, considering high risk of CKD for adverse patient outcomes.
Conclusion: This study indicate that compensated Jaffé creatinine procedure, in spite of the glucose-dependent bias, is not inferior to enzymatic creatinine in CKD diagnosis/staging and therefore may provide a reliable and cost-effective tool for the renal function assessment in diabetic patients.
Keywords: Chronic kidney disease; Chronic kidney disease-Epidemiology Collaboration Group; Compensated Jaffé method; Creatinine; Diabetes; Enzymatic method; Estimated glomerular filtration rate; Impact.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article are reported.
Figures
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation. Brussels: IDF; 2015. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 7th edition.
-
- National Kidney Foundation. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int Suppl. 2013;3:1–150.
-
- American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes--2014. Diabetes Care. 2014;37 Suppl 1:S14–S80. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

