ANTITUMOR AND APOPTOTIC EFFECTS OF CUCURBITACIN A IN A-549 LUNG CARCINOMA CELLS IS MEDIATED VIA G2/M CELL CYCLE ARREST AND M-TOR/PI3K/AKT SIGNALLING PATHWAY
- PMID: 28573224
- PMCID: PMC5446468
- DOI: 10.21010/ajtcam.v14i2.9
ANTITUMOR AND APOPTOTIC EFFECTS OF CUCURBITACIN A IN A-549 LUNG CARCINOMA CELLS IS MEDIATED VIA G2/M CELL CYCLE ARREST AND M-TOR/PI3K/AKT SIGNALLING PATHWAY
Abstract
Background: The main aim of this study was to demonstrate the antitumor potential of cucurbitacin A on A-549 NSCLC (non-small cell lung cancer cells). The effects of Cucurbitacin A on apoptotic induction, cell physic, cell cycle failure and m-TOR/PI3K/Akt signalling pathway were also investigated in the present study.
Materials and methods: MTT assay and clonogenic assay were carried out to study effects of this compound on cell cytotoxicity and colony forming tendency in A-549 cells. Moreover, phase and fluorescence microscopic techniques were used to examine the effects on cell morphology and induction of apoptosis. The effects on cell cycle phase distribution were investigated by flow cytometry and effects on m-TOR/PI3K/Akt signalling proteins were assessed by western blot analysis.
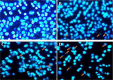
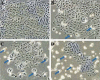
Results: Results showed that cucurbitacin A induced dose-dependent cytotoxic effects along with suppressing the colony forming tendency in these cells. Cucurbitacin A also induced morphological changes in these cells featuring chromatin condensation, cell shrinkage and apoptotic body formation. G2/M phase cell cycle collapse was also induced by Cucurbitacin A along with inhibition of expression levels of m-TOR/PI3K/Akt proteins.
Conclusions: In conclusion, cucurbitacin A inhibits cancer growth in A-549 NSCLC cells by inducing apoptosis, targeting m-TOR/PI3K/Akt signalling pathway and G2/M cell cycle.
Keywords: Non-small cell lung cancer; antitumor activity; apoptosis; cell cycle; cucurbitacin A.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest
Figures





Similar articles
-
Apoptosis induced by the methanol extract of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge in non-small cell lung cancer through PTEN-mediated inhibition of PI3K/Akt pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Mar 22;200:107-116. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.12.051. Epub 2017 Jan 12. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28088493
-
Anticancer effects of kaempferol in A375 human malignant melanoma cells are mediated via induction of apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, inhibition of cell migration and downregulation of m-TOR/PI3K/AKT pathway.J BUON. 2018 Jan-Feb;23(1):218-223. J BUON. 2018. PMID: 29552787
-
Naturally occurring aesculetin coumarin exerts antiproliferative effects in gastric cancer cells mediated via apoptotic cell death, cell cycle arrest and targeting PI3K/AKT/M-TOR signalling pathway.Acta Biochim Pol. 2021 Mar 17;68(1):109-113. doi: 10.18388/abp.2020_5463. Acta Biochim Pol. 2021. PMID: 33728889
-
Cucurbitacins: A Systematic Review of the Phytochemistry and Anticancer Activity.Am J Chin Med. 2015;43(7):1331-50. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X15500755. Epub 2015 Oct 27. Am J Chin Med. 2015. PMID: 26503558
-
Apoptotic and antimetastatic effect of cucurbitacins in cancer: recent trends and advancement.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023 Sep;396(9):1867-1878. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02471-z. Epub 2023 Apr 3. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37010571 Review.
Cited by
-
Cucurbitacins as Potent Chemo-Preventive Agents: Mechanistic Insight and Recent Trends.Biomolecules. 2022 Dec 27;13(1):57. doi: 10.3390/biom13010057. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36671442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of Cytoskeleton, Protein Trafficking, and Signaling Pathways by Metabolites from Cucurbitaceae, Ericaceae, and Rosaceae Plant Families.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Nov 10;15(11):1380. doi: 10.3390/ph15111380. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36355554 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of cucurbitacins for lung cancer research and therapy.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2021 Jul;88(1):1-14. doi: 10.1007/s00280-021-04265-7. Epub 2021 Apr 6. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33825035 Review.
-
Recent Advances in the Application of Cucurbitacins as Anticancer Agents.Metabolites. 2023 Oct 14;13(10):1081. doi: 10.3390/metabo13101081. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 37887406 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bader AG, Kang S, Zhao L, Vogt PK. Oncogenic PI3K deregulates transcription and translation. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2005;5:921–9. - PubMed
-
- Chen X, Bao J, Guo J, Ding Q, Lu J, Huang M, Wang Y. Biological activities and potential molecular targets of cucurbitacins: a focus on cancer. Anti-Cancer Drugs. 2012;23(8):777–787. - PubMed
-
- Chen JC, Chiu MH, Nie RL, Cordell GA, Qiu SX. Cucurbitacins and cucurbitane glycosides: structures and biological activities. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2005;22:386–399. - PubMed
-
- Doyle LA. Mechanisms of drug resistance in human lung cancer cells. Semin. Oncol. 1993;20:326–37. - PubMed
-
- Engelman JA, Luo J, Cantley LC. The evolution of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases as regulators of growth and metabolism. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006;7:606–19. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
