ANALYSIS OF PHENOLIC AND FLAVONOIDS OF WILD EPHEDRA ALATA PLANT EXTRACTS BY LC/PDA AND LC/MS AND THEIR ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY
- PMID: 28573229
- PMCID: PMC5446436
- DOI: 10.21010/ajtcam.v14i2.14
ANALYSIS OF PHENOLIC AND FLAVONOIDS OF WILD EPHEDRA ALATA PLANT EXTRACTS BY LC/PDA AND LC/MS AND THEIR ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY
Abstract
Background: Ephedra is among Palestinian medicinal plants that are traditionally used in folkloric medicine for treating many diseases. Ephedra is known to have antibacterial and antioxidant effects. The goal of this study is to evaluate the antioxidant activity of different extracts from the Ephedra alata plant growing wild in Palestine, and to analyze their phenolic and flavonoid constituents by HPLC/PDA and HPLC/MS.
Materials and methods: Samples of the Ephedra alata plant grown wild in Palestine were extracted with three different solvents namely, 100% water, 80% ethanol, and 100% ethanol. The extracts were analyzed for their total phenolic content (TPC), total flavonoid content (TFC), antioxidant activity (AA), as well as phenolic and flavonoids content by HPLC/PDA/MS.
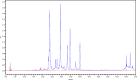
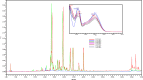
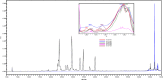
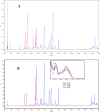
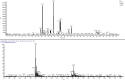
Results: The results revealed that the polarity of the extraction solvent affects the TPC, TFC, and AA of extracts. It was found that both TPC and AA are highest for plant extracted with 80% ethanol, followed by 100% ethanol, and finally with 100% water. TFC however was highest in the following order: 100% ethanol > 80% ethanol > water. Pearson correlation indicated that there is a significant correlation between AA and TPC, but there is no correlation between AA and TFC. Simultaneous HPLC-PDA and UHPLC-MS analysis of the ethanolic plant extracts revealed the presence of Luteolin-7-O-glucuronide flavone, Myricetin 3-rhamnoside and some other major polyphenolic compounds that share myricetin skeleton.
Conclusion: Ephedra alata extract is rich in potent falvonoid glycosidic compounds as revealed by their similar overlaid UV-Vis spectra and UHPLC-MS results. On the basis of these findings, it is concluded that Ephedra alata constitutes a natural source of potent antioxidants that may prevent many diseases and could be potentially used in food, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical products.
Keywords: Ephedra Alata; HPLC; LC/MS; antioxidant activity; flavonoid content; phenolic content.
Figures
References
-
- Alali FQ, Tawaha K, El-Elimat T, Syouf M, El-Fayad M, Abulaila K, Nielsen SJ, Wheaton WD, Falkinham J. O, III, Oberlies NH. Antioxidant activity and total phenolic content of aqueous and methanolic extracts of Jordanian plants: an ICBG project’. Natural Product Research. 2007;21:1121–1131. - PubMed
-
- Apak R, Guclu K, Ozyurek M, Celik SE. Mechanism of antioxidant capacity assays and the CUPRAC (cupric ion reducing antioxidant capacity) assay. Microchim. Acta. 2008;160:413–419.
-
- Benzie IF.F, Strain JJ. Ferric reducing/antioxidant power assay: Direct measure of total antioxidant activity of biological fluids and modified version for simultaneous measurement of total antioxidant power and ascorbic acid concentration. Methods In Enzymology. 1999;299:15–27. - PubMed
-
- Brand-Williams W, Cuvelier ME, Berset C. Use of free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. Lebensm. Wiss. Technol. 1995;28:25–30.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
