PROTECTIVE EFFECT OF MORINGA PEREGRINA LEAVES EXTRACT ON ACETAMINOPHEN -INDUCED LIVER TOXICITY IN ALBINO RATS
- PMID: 28573237
- PMCID: PMC5446445
- DOI: 10.21010/ajtcam.v14i2.22
PROTECTIVE EFFECT OF MORINGA PEREGRINA LEAVES EXTRACT ON ACETAMINOPHEN -INDUCED LIVER TOXICITY IN ALBINO RATS
Abstract
Background: Acetaminophen is a common antipyretic drug but at overdose can cause severe hepatotoxicity that may further develop into liver failure and hepatic centrilobular necrosis in experimental animals and humans. This study was undertaken to assess the ameliorative role of Moringa peregrina leaves extract against acetaminophen toxicity in rats.
Materials and methods: Induction of hepatotoxicity was done by chronic oral administration of acetaminophen (750 mg/kg bwt) for 4 weeks. To study the possible hepatoprotective effect, Moringa peregrina leaves extract (200 mg/kg bwt) or Silymarin (50 mg/kg bwt) was administered orally, for 4 weeks, along with acetaminophen.
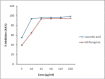
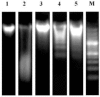
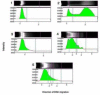
Results: acetaminophen significantly increased serum liver enzymes and caused oxidative stress, evidenced by significantly increased tissue malondialdehyde, glutathione peroxidase, hepatic DNA fragmentation, and significant decrease of glutathione and antioxidant enzymes in liver, blood and brain. On the other hand, administration of Moringa peregrina leaves extract reversed acetaminophen-related toxic effects through: powerful malondialdehyde suppression, glutathione peroxidase normalization and stimulation of the cellular antioxidants synthesis represented by significant increase of glutathione, catalase and superoxide dismutase in liver, blood and brain, besides, DNA fragmentation was significantly decreased in the liver tissue.
Conclusion: acetaminophen induced oxidative damage can be improved by Moringa peregrina leaves extract-treatment, due to its antioxidant potential.
Keywords: Antioxidant; DNA fragmentation; Moringaceae; NAPQI; Oxidative stress.
Figures

References
-
- Aebi H. Catalase in-vitro. In: Packer L, editor. Methods of enzymology. Vol. 105. San Diego: Academic Press Inc; 1984. pp. 121–6. - PubMed
-
- Ali SI, Said MM, Hassan EK. Prophylactic and curative effects of purslane on bile duct ligation-induced hepatic fibrosis in albino rats. Ann. Hepatol. 2011;10(3):340–346. - PubMed
-
- Batanouny KH, shabana M, Aboutabl E, Soliman F. Wild Medicinal Plants in Egypt. Palm press; Cairo, Egypt: 1999. p. 151.
-
- Belfield A, Goldberg DM. Revised assay for serum phenyl phosphatase activity using 4-amino-antipyrine. Enzyme. 1971;12:561–573. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
