THE USE OF RHEUM PALMATUM L. IN THE TREATMENT OF ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME: A META-ANALYSIS OF RANDOMIZED, CONTROLLED TRIALS
- PMID: 28573250
- PMCID: PMC5446460
- DOI: 10.21010/ajtcam.v14i2.35
THE USE OF RHEUM PALMATUM L. IN THE TREATMENT OF ACUTE RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME: A META-ANALYSIS OF RANDOMIZED, CONTROLLED TRIALS
Abstract
Background: Chinese medicine theory shows that "lung being connected with large intestine", and the modern western medicine also shows that the lung and intestinal tract affect each other in physiological and pathological conditions. If the lung ventilation dysfunction is caused by inflammatory exudate or secretions obstruction of the small airway ventilation, blood gas partial pressure is increased and intestinal gas absorption difficulty may lead to intestinal inflation and dysfunction (Wang N et al., 2011). Rheum palmatum L. can play the roles of anti-coagulation and anti-thrombosis, and improve microcirculation through lowering the endotoxin-induced permeability of microvascular tissue, reducing tissue oedema, decreasing inflammatory exudation and necrosis, and enhancing cyto-protection mechanism (Yang TZ et al., 2014). Therefore, systemic evaluation of the evidence pertaining to the usage of Rheum palmatum L. in treating acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) has significant clinical significance.
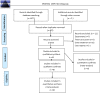
Materials and methods: Various Electronic Databases CBM, CNKI, VIP, Wanfang, PubMed and Cochrane Library were searched until December 2015. Numerous randomized-controlled trials (RCTs) evaluating the efficacy of Rheum palmatum L. for the treatment of acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome were collected. The quality of the included studies was evaluated and a meta-analysis was performed using the RevMan5.0 software.
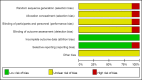
Results: Eight RCTs involving 489 patients were selected for this review. The results of the Meta-analysis revealed that Rheum palmatum L. therapy, combined with routine comprehensive treatment, was significantly superior to that of routine comprehensive treatment alone, in the areas of decreasing mortality, the mechanical ventilation time, the level of interleukin-6,8 and the untoward effect, and also in improving arterial blood gas (PaO2/FiO2, PaO2) (P<0.05).
Conclusion: Compared with treatment with routine comprehensive alone, Rheum palmatum L. treatment combined with routine comprehensive, has been shown to effectively decrease the mortality, mechanical ventilation time and ameliorate the arterial blood gas, the cytokine levels, and the untoward effect. However, the evidence appears not to be very compelling due to the poor quality of the original studies.
Keywords: ALI/ARDS; Meta-analysis; Rheum palmatum L; Systematic Review; Western medicine therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that would prejudice the impartiality.
Figures








References
-
- ARDS Definition Task Force. Ranieri VM, Rubenfeid Thompson BT, Ferquson ND, Caldwell E, Fan E, Camporota L, Slutsky AS. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Berlin Definition. JAMA. 2012;307:2526–2533. - PubMed
-
- Altuntas CZ, Johnson JM, Tuohy VK. Autoimmune targeted disruption of the pituitary-ovarian axis causes premature ovarian failure. J Immunol. 2006;177:1998–1996. - PubMed
-
- Bernard GR, Artigas A, Brigham KL, Carlet J, Falke K, Hudson L, Lamy M, Legall JR, Morris A, Spragg R. The American-European Consensus Conference on ARDS. Definitions, mechanisms, relevant outcomes, and clinical trial coordination. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994;149:818–824. - PubMed
-
- Cui G, Huang K, Jing K, Zhang DS, Zhang DY. The curative effect observation of combination of traditional Chinese and western medicine on ARDS after chest trauma. Liaoning journal of traditional Chinese medicine. 2011;38:1166–1167.
-
- Feng J, Zhou M. Clinical observation on Rheum palmatum L. in the complex treatment for ARDS. Chinese archives of traditional Chinese medicine. 2012;30:1568–1569.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
