Lipid Internal Dynamics Probed in Nanodiscs
- PMID: 28573816
- PMCID: PMC5697661
- DOI: 10.1002/cphc.201700450
Lipid Internal Dynamics Probed in Nanodiscs
Abstract
Nanodiscs offer a very promising tool to incorporate membrane proteins into native-like lipid bilayers and an alternative to liposomes to maintain protein functions and protein-lipid interactions in a soluble nanoscale object. The activity of the incorporated membrane protein appears to be correlated to its dynamics in the lipid bilayer and by protein-lipid interactions. These two parameters depend on the lipid internal dynamics surrounded by the lipid-encircling discoidal scaffold protein that might differ from more unrestricted lipid bilayers observed in vesicles or cellular extracts. A solid-state NMR spectroscopy investigation of lipid internal dynamics and thermotropism in nanodiscs is reported. The gel-to-fluid phase transition is almost abolished for nanodiscs, which maintain lipid fluid properties for a large temperature range. The addition of cholesterol allows fine-tuning of the internal bilayer dynamics by increasing chain ordering. Increased site-specific order parameters along the acyl chain reflect a higher internal ordering in nanodiscs compared with liposomes at room temperature; this is induced by the scaffold protein, which restricts lipid diffusion in the nanodisc area.
Keywords: NMR spectroscopy; lipids; membranes; nanostructures; solid-state structures.
© 2017 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures

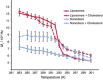


References
-
- Bayburt T. H., Carlson J. W., Sligar S. G., J. Struct. Biol. 1998, 123, 37–44. - PubMed
-
- Bayburt T. H., Grinkova Y. V., Sligar S. G., Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 853–856.
-
- Bibow S., Polyhach Y., Eichmann C., Chi C. N., Kowal J., Albiez S., McLeod R. A., Stahlberg H., Jeschke G., Güntert P., Riek R., Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2017, 24, 187–193. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

