Detection of clinically relevant copy-number variants by exome sequencing in a large cohort of genetic disorders
- PMID: 28574513
- PMCID: PMC5460076
- DOI: 10.1038/gim.2016.163
Detection of clinically relevant copy-number variants by exome sequencing in a large cohort of genetic disorders
Abstract
Purpose: Copy-number variation is a common source of genomic variation and an important genetic cause of disease. Microarray-based analysis of copy-number variants (CNVs) has become a first-tier diagnostic test for patients with neurodevelopmental disorders, with a diagnostic yield of 10-20%. However, for most other genetic disorders, the role of CNVs is less clear and most diagnostic genetic studies are generally limited to the study of single-nucleotide variants (SNVs) and other small variants. With the introduction of exome and genome sequencing, it is now possible to detect both SNVs and CNVs using an exome- or genome-wide approach with a single test.
Methods: We performed exome-based read-depth CNV screening on data from 2,603 patients affected by a range of genetic disorders for which exome sequencing was performed in a diagnostic setting.
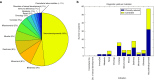
Results: In total, 123 clinically relevant CNVs ranging in size from 727 bp to 15.3 Mb were detected, which resulted in 51 conclusive diagnoses and an overall increase in diagnostic yield of ~2% (ranging from 0 to -5.8% per disorder).
Conclusions: This study shows that CNVs play an important role in a broad range of genetic disorders and that detection via exome-based CNV profiling results in an increase in the diagnostic yield without additional testing, bringing us closer to single-test genomics.Genet Med advance online publication 27 October 2016.
Figures

References
-
- Hochstenbach R, van Binsbergen E, Engelen J, et al. Array analysis and karyotyping: workflow consequences based on a retrospective study of 36,325 patients with idiopathic developmental delay in the Netherlands. Eur J Med Genet 2009;52:161–169. - PubMed
-
- Sagoo GS, Butterworth AS, Sanderson S, Shaw-Smith C, Higgins JP, Burton H. Array CGH in patients with learning disability (mental retardation) and congenital anomalies: updated systematic review and meta-analysis of 19 studies and 13,926 subjects. Genet Med 2009;11:139–146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

