The impact of EpCAM expression on response to chemotherapy and clinical outcomes in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer
- PMID: 28574829
- PMCID: PMC5546482
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.17871
The impact of EpCAM expression on response to chemotherapy and clinical outcomes in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer
Abstract
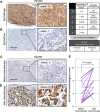
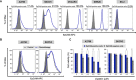
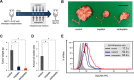
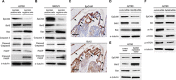
Epithelial ovarian cancer is a highly lethal malignancy; moreover, overcoming chemoresistance is the major challenging in treating ovarian cancer patients. The cancer stem cell (CSC) hypothesis considers CSCs to be the main culprits in driving tumor initiation, metastasis, and resistance to conventional therapy. Although growing evidence suggest that CSCs are responsible for chemoresistance, the contribution of CSC marker EpCAM to resistance to chemotherapy remains unresolved.Here we have demonstrated that ovarian cancers containing high levels of EpCAM have a significantly much lower probability of achieving overall responsive rates after first-line chemotherapy. In addition, multivariate analysis revealed that EpCAM expression is an independent risk factor for chemoresistance, indicating that EpCAM expression is a predictive biomarker of chemotherapeutic response. Consistent with these clinical observations, in vitro assays, we found that the subpopulation of EpCAM-positive ovarian cancer cells shows a significantly higher viability compared with EpCAM-negative cells in response to cisplatin treatment by preventing chemotherapy-induced apoptosis, which is regulated by EpCAM-Bcl-2 axis. Furthermore, in an in vivo mouse model, platinum agents preferentially eliminated EpCAM-negative cells in comparison with EpCAM-positive cells, suggesting that the remaining subpopulation of EpCAM-positive cells contributes to tumor recurrence after chemotherapy. Finally, we also found that an increased expression of EpCAM is associated with poor prognosis in ovarian cancer patients.Our findings highlight the clinical significance of EpCAM in the resistance to chemotherapy and provide a rationale for EpCAM-targeted therapy to improve chemoresistance. Targeting EpCAM should be a promising approach to effectively extirpate the CSCs as the putative root of ovarian cancer.
Keywords: EpCAM; cancer stem cell; chemoresistance; ovarian cancer; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
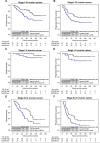
References
-
- Miranda F, Mannion D, Liu S, Zheng Y, Mangala LS, Redondo C, Herrero-Gonzalez S, Xu R, Taylor C, Chedom DF, Karaminejadranjbar M, Albukhari A, Jiang D, et al. Salt-Inducible Kinase 2 Couples Ovarian Cancer Cell Metabolism with Survival at the Adipocyte-Rich Metastatic Niche. Cancer Cell. 2016;30:273–289. - PubMed
-
- Yap TA, Carden CP, Kaye SB. Beyond chemotherapy: targeted therapies in ovarian cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:167–181. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal R, Kaye SB. Ovarian cancer: strategies for overcoming resistance to chemotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:502–516. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

