Maternal RNA regulates Aurora C kinase during mouse oocyte maturation in a translation-independent fashion
- PMID: 28575288
- PMCID: PMC6279119
- DOI: 10.1093/biolre/iox047
Maternal RNA regulates Aurora C kinase during mouse oocyte maturation in a translation-independent fashion
Abstract
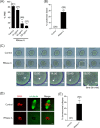
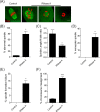
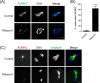
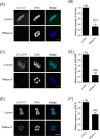
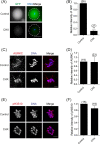
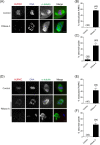
During oocyte meiotic maturation, Aurora kinase C (AURKC) is required to accomplish many critical functions including destabilizing erroneous kinetochore-microtubule (K-MT)attachments and regulating bipolar spindle assembly. How localized activity of AURKC is regulated in mammalian oocytes, however, is not fully understood. Female gametes from many species, including mouse, contain stores of maternal transcripts that are required for downstream developmental events. We show here that depletion of maternal RNA in mouse oocytes resulted in impaired meiotic progression, increased incidence of chromosome misalignment and abnormal spindle formation at metaphase I (Met I), and cytokinesis defects. Importantly, depletion of maternal RNA perturbed the localization and activity of AURKC within the chromosomal passenger complex (CPC). These perturbations were not observed when translation was inhibited by cycloheximide (CHX) treatment. These results demonstrate a translation-independent function of maternal RNA to regulate AURKC-CPC function in mouse oocytes.
Keywords: Aurora kinase C; chromosomal passenger complex; maternal RNA; meiosis; mouse oocyte.
© The Authors 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Society for the Study of Reproduction. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Jelluma N, Brenkman AB, van den Broek NJ, Cruijsen CW, van Osch MH, Lens SM, Medema RH, Kops GJ. Mps1 phosphorylates Borealin to control Aurora B activity and chromosome alignment. Cell 2008; 132:233–246. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

