A Class of Environmental and Endogenous Toxins Induces BRCA2 Haploinsufficiency and Genome Instability
- PMID: 28575672
- PMCID: PMC5457488
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.05.010
A Class of Environmental and Endogenous Toxins Induces BRCA2 Haploinsufficiency and Genome Instability
Abstract
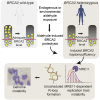
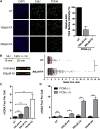
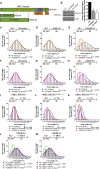
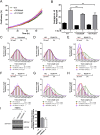
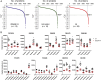
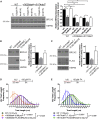
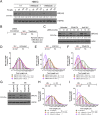
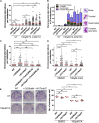
Mutations truncating a single copy of the tumor suppressor, BRCA2, cause cancer susceptibility. In cells bearing such heterozygous mutations, we find that a cellular metabolite and ubiquitous environmental toxin, formaldehyde, stalls and destabilizes DNA replication forks, engendering structural chromosomal aberrations. Formaldehyde selectively depletes BRCA2 via proteasomal degradation, a mechanism of toxicity that affects very few additional cellular proteins. Heterozygous BRCA2 truncations, by lowering pre-existing BRCA2 expression, sensitize to BRCA2 haploinsufficiency induced by transient exposure to natural concentrations of formaldehyde. Acetaldehyde, an alcohol catabolite detoxified by ALDH2, precipitates similar effects. Ribonuclease H1 ameliorates replication fork instability and chromosomal aberrations provoked by aldehyde-induced BRCA2 haploinsufficiency, suggesting that BRCA2 inactivation triggers spontaneous mutagenesis during DNA replication via aberrant RNA-DNA hybrids (R-loops). These findings suggest a model wherein carcinogenesis in BRCA2 mutation carriers can be incited by compounds found pervasively in the environment and generated endogenously in certain tissues with implications for public health.
Keywords: BRCA2; R-loop; SWATH-MS; acetaldehyde; aldehyde; formaldehyde; induced haploinsufficiency; proteasomal degradation; replication stress.
Copyright © 2017 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
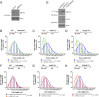
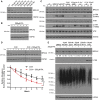
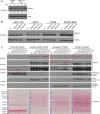
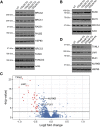
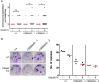
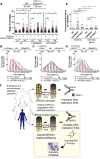
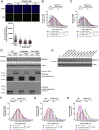
Comment in
-
Aldehydes Pose a Threat to BRCA2 Mutation Carriers.Cell. 2017 Jun 1;169(6):979-981. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.05.021. Cell. 2017. PMID: 28575676
-
Thwarting endogenous stress: BRCA protects against aldehyde toxicity.EMBO Mol Med. 2017 Oct;9(10):1331-1333. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201708194. EMBO Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28835508 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bhatia V., Barroso S.I., García-Rubio M.L., Tumini E., Herrera-Moyano E., Aguilera A. BRCA2 prevents R-loop accumulation and associates with TREX-2 mRNA export factor PCID2. Nature. 2014;511:362–365. - PubMed
-
- Breast Cancer Linkage Consortium Cancer risks in BRCA2 mutation carriers. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1999;91:1310–1316. - PubMed
-
- Chitta K., Paulus A., Akhtar S., Blake M.K., Caulfield T.R., Novak A.J., Ansell S.M., Advani P., Ailawadhi S., Sher T. Targeted inhibition of the deubiquitinating enzymes, USP14 and UCHL5, induces proteotoxic stress and apoptosis in Waldenström macroglobulinaemia tumour cells. Br. J. Haematol. 2015;169:377–390. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

