Genome editing of factor X in zebrafish reveals unexpected tolerance of severe defects in the common pathway
- PMID: 28576875
- PMCID: PMC5542852
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2017-02-765206
Genome editing of factor X in zebrafish reveals unexpected tolerance of severe defects in the common pathway
Abstract
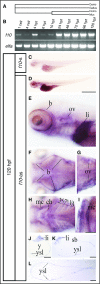
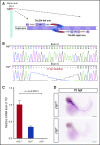
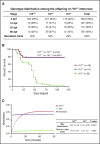
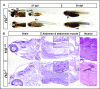
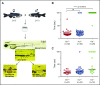
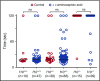
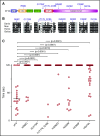
Deficiency of factor X (F10) in humans is a rare bleeding disorder with a heterogeneous phenotype and limited therapeutic options. Targeted disruption of F10 and other common pathway factors in mice results in embryonic/neonatal lethality with rapid resorption of homozygous mutants, hampering additional studies. Several of these mutants also display yolk sac vascular defects, suggesting a role for thrombin signaling in vessel development. The zebrafish is a vertebrate model that demonstrates conservation of the mammalian hemostatic and vascular systems. We have leveraged these advantages for in-depth study of the role of the coagulation cascade in the developmental regulation of hemostasis and vasculogenesis. In this article, we show that ablation of zebrafish f10 by using genome editing with transcription activator-like effector nucleases results in a major embryonic hemostatic defect. However, widespread hemorrhage and subsequent lethality does not occur until later stages, with absence of any detectable defect in vascular development. We also use f10-/- zebrafish to confirm 5 novel human F10 variants as causative mutations in affected patients, providing a rapid and reliable in vivo model for testing the severity of F10 variants. These findings as well as the prolonged survival of f10-/- mutants will enable us to expand our understanding of the molecular mechanisms of hemostasis, including a platform for screening variants of uncertain significance in patients with F10 deficiency and other coagulation disorders. Further study as to how fish tolerate what is an early lethal mutation in mammals could facilitate improvement of diagnostics and therapeutics for affected patients with bleeding disorders.
© 2017 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: J.A.S. has been a consultant for Bayer, Shire, CSL Behring, Grifols, and Octopharma. F.P. has received honoraria for participating as a speaker at satellite symposia and educational meetings organized by Bayer, Biotest, CSL Behring, Grifols, Novo Nordisk, and Sobi; is the recipient of research grant funding from Alexion, Biotest, Kedrion Biopharma, and Novo Nordisk paid to Fondazione Luigi Villa; and has received consulting fees from Kedrion Biopharma, LFB, and Octapharma. She is member of the Ablynx scientific advisory board. J.K.J. has financial interests in Beacon Genomics, Beam Therapeutics, Editas Medicine, Poseida Therapeutics, and Transposagen Biopharmaceuticals. J.K.J.’s interests were reviewed and are managed by Massachusetts General Hospital and Partners HealthCare in accordance with their conflict-of-interest policies. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Zebrafish factor 10 and the life aquatic.Blood. 2017 Aug 3;130(5):563-565. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-06-789149. Blood. 2017. PMID: 28775159 No abstract available.
References
-
- Furie B, Furie BC. The molecular basis of blood coagulation. Cell. 1988;53(4):505-518. - PubMed
-
- Menegatti M, Peyvandi F. Factor X deficiency. Semin Thromb Hemost. 2009;35(4):407-415. - PubMed
-
- Di Scipio RG, Hermodson MA, Yates SG, Davie EW. A comparison of human prothrombin, factor IX (Christmas factor), factor X (Stuart factor), and protein S. Biochemistry. 1977;16(4):698-706. - PubMed
-
- van Dieijen G, Tans G, Rosing J, Hemker HC. The role of phospholipid and factor VIIIa in the activation of bovine factor X. J Biol Chem. 1981;256(7):3433-3442. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

