Crystal structure of tubulin tyrosine ligase-like 3 reveals essential architectural elements unique to tubulin monoglycylases
- PMID: 28576883
- PMCID: PMC5488916
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1617286114
Crystal structure of tubulin tyrosine ligase-like 3 reveals essential architectural elements unique to tubulin monoglycylases
Abstract
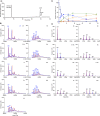
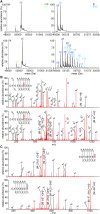
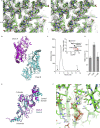
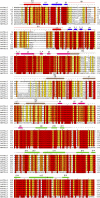
Glycylation and glutamylation, the posttranslational addition of glycines and glutamates to genetically encoded glutamates in the intrinsically disordered tubulin C-terminal tails, are crucial for the biogenesis and stability of cilia and flagella and play important roles in metazoan development. Members of the diverse family of tubulin tyrosine ligase-like (TTLL) enzymes catalyze these modifications, which are part of an evolutionarily conserved and complex tubulin code that regulates microtubule interactions with cellular effectors. The site specificity of TTLL enzymes and their biochemical interplay remain largely unknown. Here, we report an in vitro characterization of a tubulin glycylase. We show that TTLL3 glycylates the β-tubulin tail at four sites in a hierarchical order and that TTLL3 and the glutamylase TTLL7 compete for overlapping sites on the tubulin tail, providing a molecular basis for the anticorrelation between glutamylation and glycylation observed in axonemes. This anticorrelation demonstrates how a combinatorial tubulin code written in two different posttranslational modifications can arise through the activities of related but distinct TTLL enzymes. To elucidate what structural elements differentiate TTLL glycylases from glutamylases, with which they share the common TTL scaffold, we determined the TTLL3 X-ray structure at 2.3-Å resolution. This structure reveals two architectural elements unique to glycyl initiases and critical for their activity. Thus, our work sheds light on the structural and functional diversification of TTLL enzymes, and constitutes an initial important step toward understanding how the tubulin code is written through the intersection of activities of multiple TTLL enzymes.
Keywords: TTLL enzymes; glutamylation; glycylation; tubulin code; tubulin modification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Verhey KJ, Gaertig J. The tubulin code. Cell Cycle. 2007;6:2152–2160. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

