Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 3 and RhoA signaling mediate inflammatory gene expression in astrocytes
- PMID: 28577576
- PMCID: PMC5455202
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-017-0882-x
Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 3 and RhoA signaling mediate inflammatory gene expression in astrocytes
Abstract
Background: Sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) signals through G protein-coupled receptors to elicit a wide range of cellular responses. In CNS injury and disease, the blood-brain barrier is compromised, causing leakage of S1P from blood into the brain. S1P can also be locally generated through the enzyme sphingosine kinase-1 (Sphk1). Our previous studies demonstrated that S1P activates inflammation in murine astrocytes. The S1P1 receptor subtype has been most associated with CNS disease, particularly multiple sclerosis. S1P3 is most highly expressed and upregulated on astrocytes, however, thus we explored the involvement of this receptor in inflammatory astrocytic responses.
Methods: Astrocytes isolated from wild-type (WT) or S1P3 knockout (KO) mice were treated with S1P3 selective drugs or transfected with short interfering RNA to determine which receptor subtypes mediate S1P-stimulated inflammatory responses. Interleukin-6 (IL-6), and vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFa) messenger RNA (mRNA) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) mRNA and protein were assessed by q-PCR and Western blotting. Activation of RhoA was measured using SRE.L luciferase and RhoA implicated in S1P signaling by knockdown of Gα12/13 proteins or by inhibiting RhoA activation with C3 exoenzyme. Inflammation was simulated by in vitro scratch injury of cultured astrocytes.
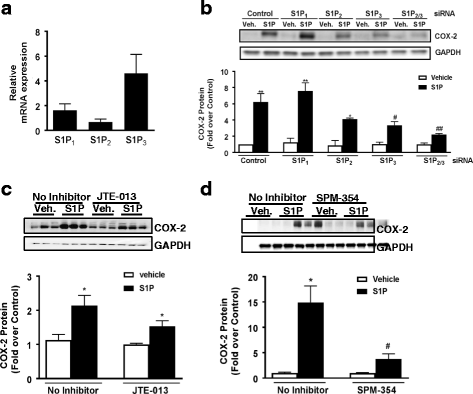
Results: S1P3 was highly expressed in astrocytes and further upregulated in response to simulated inflammation. Studies using S1P3 knockdown and S1P3 KO astrocytes demonstrated that S1P3 mediates activation of RhoA and induction of COX-2, IL-6, and VEGFa mRNA, with some contribution from S1P2. S1P induces expression of all of these genes through coupling to the Gα12/13 proteins which activate RhoA. Studies using S1P3 selective agonists/antagonists as well as Fingolimod (FTY720) confirmed that stimulation of S1P3 induces COX-2 expression in astrocytes. Simulated inflammation increased expression of Sphk1 and consequently activated S1P3, demonstrating an autocrine pathway through which S1P is formed and released from astrocytes to regulate COX-2 expression.
Conclusions: S1P3, through its ability to activate RhoA and its upregulation in astrocytes, plays a unique role in inducing inflammatory responses and should be considered as a potentially important therapeutic target for CNS disease progression.
Keywords: Astrocytes; Central nervous system; Inflammation; RhoA; S1P; S1P3.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Selective coupling of the S1P3 receptor subtype to S1P-mediated RhoA activation and cardioprotection.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2017 Feb;103:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2016.12.008. Epub 2016 Dec 23. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28017639 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingosine 1-phosphate elicits RhoA-dependent proliferation and MRTF-A mediated gene induction in CPCs.Cell Signal. 2016 Aug;28(8):871-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2016.04.006. Epub 2016 Apr 14. Cell Signal. 2016. PMID: 27094722 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand-dependent inhibition of B16 melanoma cell migration and invasion via endogenous S1P2 G protein-coupled receptor. Requirement of inhibition of cellular RAC activity.J Biol Chem. 2003 Aug 29;278(35):32841-51. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M305024200. Epub 2003 Jun 16. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12810709
-
Sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling and biological activities in the cardiovascular system.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Sep;1781(9):483-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2008.04.003. Epub 2008 Apr 22. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 18472021 Review.
-
Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor signalling in the heart.Cardiovasc Res. 2009 May 1;82(2):193-200. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvp086. Epub 2009 Mar 12. Cardiovasc Res. 2009. PMID: 19282351 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of Sphingosine Kinase 1 Reduces Sphingosine-1-Phosphate and Exacerbates Amyloid-Beta-Induced Neuronal Cell Death in Mixed-Glial-Cell Culture.Neurol Int. 2024 Jul 4;16(4):709-730. doi: 10.3390/neurolint16040054. Neurol Int. 2024. PMID: 39051215 Free PMC article.
-
[Disease-modifying treatment of secondary progressive multiple sclerosis].Nervenarzt. 2021 Oct;92(10):1052-1060. doi: 10.1007/s00115-021-01080-6. Epub 2021 Mar 3. Nervenarzt. 2021. PMID: 33656569 Free PMC article. Review. German.
-
S1P/S1P Receptor Signaling in Neuromuscolar Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 17;20(24):6364. doi: 10.3390/ijms20246364. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31861214 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sphingosine-1-phosphate Signalling in Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Haemorrhage: Basic Science to Clinical Translation.Transl Stroke Res. 2024 Apr;15(2):352-363. doi: 10.1007/s12975-023-01133-9. Epub 2023 Feb 7. Transl Stroke Res. 2024. PMID: 36749550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Signaling in Ischemic Stroke: From Bench to Bedside and Beyond.Front Cell Neurosci. 2021 Nov 30;15:781098. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.781098. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34916911 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yatomi Y, Ohmori T, Rile G, Kazama F, Okamoto H, Sano T, Satoh K, Kume S, Tigyi G, Igarashi Y, Ozaki Y. Sphingosine 1-phosphate as a major bioactive lysophospholipid that is released from platelets and interacts with endothelial cells. Blood. 2000;96:3431–3438. - PubMed
-
- Yatomi Y, Igarashi Y, Yang L, Hisano N, Qi R, Asazuma N, Satoh K, Ozaki Y, Kume S. Sphingosine 1-phosphate, a bioactive sphingolipid abundantly stored in platelets, is a normal constituent of human plasma and serum. J Biochem. 1997;121:969–973. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a021681. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

