What is the frequency of anatomical variations and pathological findings in maxillary sinuses among patients subjected to maxillofacial cone beam computed tomography? A systematic review
- PMID: 28578369
- PMCID: PMC5549512
- DOI: 10.4317/medoral.21456
What is the frequency of anatomical variations and pathological findings in maxillary sinuses among patients subjected to maxillofacial cone beam computed tomography? A systematic review
Abstract
Background: When considering dental implant rehabilitation in atrophic posterior sectors, the maxillary sinuses must be evaluated in detail. Knowledge of the anatomical variations and of the potential lesions found in these structures conditions the outcome of sinus lift procedures and therefore of the dental implants. A systematic review is made to determine the frequency of anatomical variations and pathological findings in maxillary sinuses among patients subjected to cone beam computed tomography (CBCT).
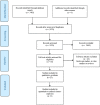
Material and methods: A PubMed (MEDLINE) literature search was made of articles published up until 20 December 2015. The systematic review was conducted based on the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analysis (PRISMA). The quality of the studies included in the review was assessed using the Methodological Index for Nonrandomized Studies (MINORS).
Results: The combinations of search terms resulted in a list of 3482 titles. Twenty-three studies finally met the inclusion criteria and were entered in the systematic review, comprising a total of 11,971 patients. The most common anatomical variations were pneumatization and sinus septa. The prevalence of maxillary sinus disease ranged from 7.5% to 66%. The most common pathological findings of the maxillary sinus were mucosal thickening, sinusitis and sinus opacification.
Conclusions: Although the main indication of CBCT of the maxillary sinus in dentistry is sinus floor elevation/treatment planning and evaluation prior to dental implant placement, this imaging modality is increasingly also used for endodontic and periodontal purposes. There is no consensus regarding the cutoff point beyond which mucosal thickening of the maxillary sinus should be regarded as pathological, and the definition of maxillary sinusitis moreover varies greatly in the scientific literature. In this regard, international consensus is required in relation to these concepts, with a clear distinction between healthy and diseased maxillary sinuses.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Incidence of anatomical variations and disease of the maxillary sinuses as identified by cone beam computed tomography: a systematic review.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2014 Nov-Dec;29(6):1301-14. doi: 10.11607/jomi.3644. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2014. PMID: 25397794
-
Effect of maxillary sinus augmentation on the survival of endosseous dental implants. A systematic review.Ann Periodontol. 2003 Dec;8(1):328-43. doi: 10.1902/annals.2003.8.1.328. Ann Periodontol. 2003. PMID: 14971260
-
Infraorbital canal variants and its clinical and surgical implications. A systematic review.Surg Radiol Anat. 2024 Jul;46(7):1027-1046. doi: 10.1007/s00276-024-03348-3. Epub 2024 Apr 29. Surg Radiol Anat. 2024. PMID: 38684553
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Eliciting adverse effects data from participants in clinical trials.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 16;1(1):MR000039. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000039.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29372930 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prevalence of maxillary sinus hypoplasia and association with variations in the sinonasal complex: a cone beam CT study.Clin Oral Investig. 2021 Sep;25(9):5463-5471. doi: 10.1007/s00784-021-03854-3. Epub 2021 Mar 4. Clin Oral Investig. 2021. PMID: 33661447
-
A radiologic evaluation of the incidence and morphology of maxillary sinus septa in Japanese dentate maxillae.Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019 Jun;23(2):233-237. doi: 10.1007/s10006-019-00773-2. Epub 2019 May 14. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019. PMID: 31089896
-
Evaluation of Odontogenic Maxillary Sinusitis with Cone Beam Computed Tomography: A Retrospective Study with Review of Literature.J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2019 Mar-Apr;9(2):194-204. doi: 10.4103/jispcd.JISPCD_435_18. Epub 2019 Apr 12. J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2019. PMID: 31058071 Free PMC article.
-
Computed tomography assessment of maxillary sinus hypoplasia and associated anatomical variations: a systematic review and meta-analysis of global evidence.Oral Radiol. 2024 Apr;40(2):124-137. doi: 10.1007/s11282-023-00726-2. Epub 2023 Dec 11. Oral Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38079051
-
Evaluation of maxillary sinus floor augmentation with the crestal approach and beta-tricalcium phosphate: a cone-beam computed tomography 3- to 9-year follow-up.Int J Implant Dent. 2020 Jul 10;6(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s40729-020-00225-7. Int J Implant Dent. 2020. PMID: 32648123 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bornstein MM, Seiffert C, Maestre-Ferrín L, Fodich I, Jacobs R, Buser D. An Analysis of Frequency, Morphology, and Locations of Maxillary Sinus Septa Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2016;31:280–7. - PubMed
-
- Pjetursson BE, Tan WC, Zwahlen M, Lang NP. A systematic review of the success of sinus floor elevation and survival of implants inserted in combination with sinus floor elevation. J Clin Periodontol. 2008;35:216–40. - PubMed
-
- Pjetursson BE, Rast C, Brägger U, Schmidlin K, Zwahlen M, Lang NP. Maxillary sinus floor elevation using the (transalveolar) osteotome technique with or without grafting material. Part I: Implant survival and patients' perception. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2009;20:667–76. - PubMed
-
- Tan WC, Lang NP, Zwahlen M, Pjetursson BE. A systematic review of the success of sinus floor elevation and survival of implants inserted in combination with sinus floor elevation. Part II: transalveolar technique. J Clin Periodontol. 2008;35:241–54. - PubMed
-
- von Arx T, Fodich I, Bornstein MM, Jensen SS. Perforation of the sinus membrane during sinus floor elevation: a retrospective study of frequency and possible risk factors. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2014;29:718–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous