Potential mechanisms of resistance to venetoclax and strategies to circumvent it
- PMID: 28578655
- PMCID: PMC5457565
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-017-3383-5
Potential mechanisms of resistance to venetoclax and strategies to circumvent it
Abstract
Background: Venetoclax (ABT-199), a first-in-class orally bioavailable BCL-2-selective inhibitor, was recently approved by the FDA for use in patients with 17p-deleted chronic lymphocytic leukemia who have received prior therapy. It is also being evaluated in numerous clinical trials for treating patients with various hematologic malignancies. As with any targeted cancer therapy, it is critically important to identify potential mechanisms of resistance, both for patient stratification and developing strategies to overcome resistance, either before it develops or as it emerges.
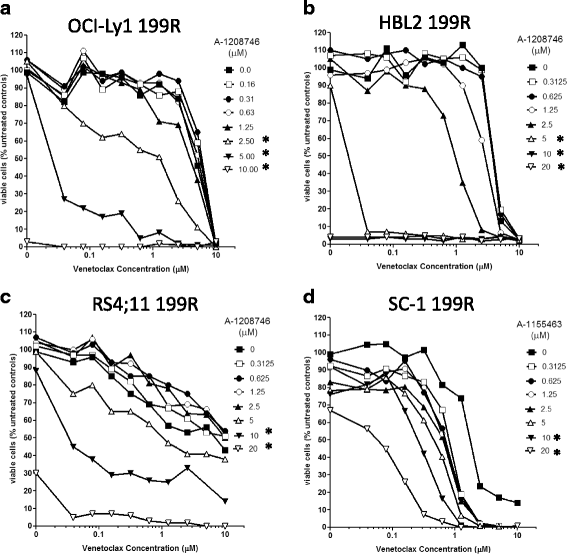
Methods: In order to gain a more comprehensive insight into the nature of venetoclax resistance mechanisms, we evaluated the changes in the BCL-2 family members at the genetic and expression levels in seven different venetoclax-resistant derived leukemia and lymphoma cell lines.
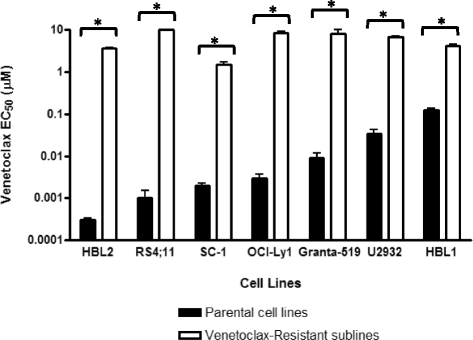
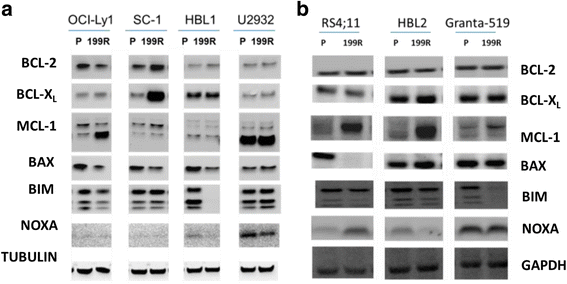
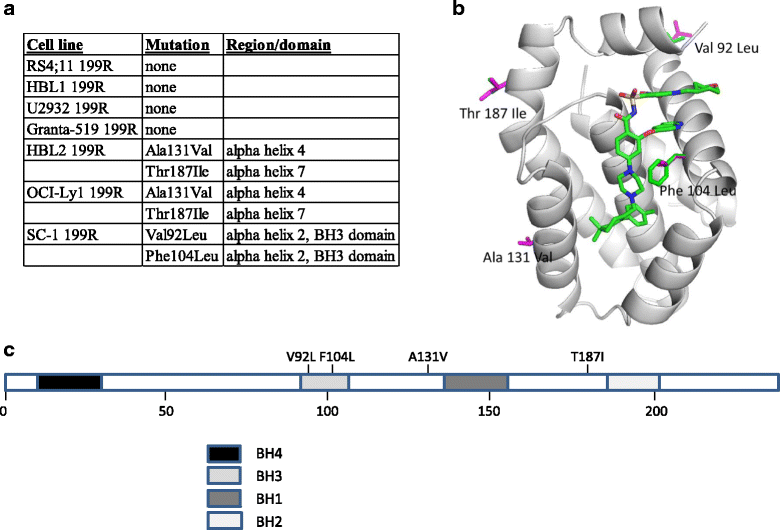
Results: Gene and protein expression analyses identified a number of different alterations in the expression of pro- and anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family members. In the resistant derived cells, an increase in either or both the anti-apoptotic proteins BCL-XL or MCL-1, which are not targeted by venetoclax was observed, and either concomitant or exclusive with a decrease in one or more pro-apoptotic proteins. In addition, mutational analysis also revealed a mutation in the BH3 binding groove (F104L) that could potentially interfere with venetoclax-binding. Not all changes may be causally related to venetoclax resistance and may only be an epiphenomenon. For resistant cell lines showing elevations in BCL-XL or MCL-1, strong synergistic cell killing was observed when venetoclax was combined with either BCL-XL- or MCL-1-selective inhibitors, respectively. This highlights the importance of BCL-XL- and MCL-1 as causally contributing to venetoclax resistance.
Conclusions: Overall our study identified numerous changes in multiple resistant lines; the changes were neither mutually exclusive nor universal across the cell lines tested, thus exemplifying the complexity and heterogeneity of potential resistance mechanisms. Identifying and evaluating their contribution has important implications for both patient selection and the rational development of strategies to overcome resistance.
Keywords: Apoptosis; BCL-2; BCL-XL; MCL-1.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression Profile of BCL-2, BCL-XL, and MCL-1 Predicts Pharmacological Response to the BCL-2 Selective Antagonist Venetoclax in Multiple Myeloma Models.Mol Cancer Ther. 2016 May;15(5):1132-44. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0730. Epub 2016 Mar 3. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016. PMID: 26939706
-
MCL-1 and BCL-xL-dependent resistance to the BCL-2 inhibitor ABT-199 can be overcome by preventing PI3K/AKT/mTOR activation in lymphoid malignancies.Cell Death Dis. 2015 Jan 15;6(1):e1593. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.525. Cell Death Dis. 2015. PMID: 25590803 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneous Pattern of Dependence on Anti-Apoptotic BCL-2 Family Proteins upon CHOP Treatment in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 30;20(23):6036. doi: 10.3390/ijms20236036. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31801186 Free PMC article.
-
Pathways and mechanisms of venetoclax resistance.Leuk Lymphoma. 2017 Sep;58(9):1-17. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2017.1283032. Epub 2017 Jan 31. Leuk Lymphoma. 2017. PMID: 28140720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutics targeting Bcl-2 in hematological malignancies.Biochem J. 2017 Oct 23;474(21):3643-3657. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20170080. Biochem J. 2017. PMID: 29061914 Review.
Cited by
-
CS2164 and Venetoclax Show Synergistic Antitumoral Activities in High Grade B-Cell Lymphomas With MYC and BCL2 Rearrangements.Front Oncol. 2021 Mar 10;11:618908. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.618908. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33777762 Free PMC article.
-
Bone marrow stroma cells promote induction of a chemoresistant and prognostic unfavorable S100A8/A9high AML cell subset.Blood Adv. 2022 Nov 8;6(21):5685-5697. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2021005938. Blood Adv. 2022. PMID: 35390134 Free PMC article.
-
A novel CDK9 inhibitor increases the efficacy of venetoclax (ABT-199) in multiple models of hematologic malignancies.Leukemia. 2020 Jun;34(6):1646-1657. doi: 10.1038/s41375-019-0652-0. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Leukemia. 2020. PMID: 31827241 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis: a Janus bifrons in T-cell immunotherapy.J Immunother Cancer. 2023 Apr;11(4):e005967. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-005967. J Immunother Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37055217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhancing venetoclax activity in hematological malignancies.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2020 Jul;29(7):697-708. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2020.1789588. Epub 2020 Jul 16. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32600066 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tse C, Shoemaker AR, Adickes J, Anderson MG, Chen J, Jin S, et al. ABT-263: a potent and orally bioavailable Bcl-2 family inhibitor. Cancer Res. 2008;68:3421–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

