SGLT2 Inhibition by Empagliflozin Promotes Fat Utilization and Browning and Attenuates Inflammation and Insulin Resistance by Polarizing M2 Macrophages in Diet-induced Obese Mice
- PMID: 28579299
- PMCID: PMC5478253
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.05.028
SGLT2 Inhibition by Empagliflozin Promotes Fat Utilization and Browning and Attenuates Inflammation and Insulin Resistance by Polarizing M2 Macrophages in Diet-induced Obese Mice
Abstract
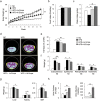
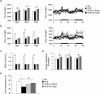
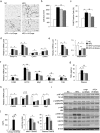
Sodium-glucose cotransporter (SGLT) 2 inhibitors increase urinary glucose excretion (UGE), leading to blood glucose reductions and weight loss. However, the impacts of SGLT2 inhibition on energy homeostasis and obesity-induced insulin resistance are less well known. Here, we show that empagliflozin, a SGLT2 inhibitor, enhanced energy expenditure and attenuated inflammation and insulin resistance in high-fat-diet-induced obese (DIO) mice. C57BL/6J mice were pair-fed a high-fat diet (HFD) or a HFD with empagliflozin for 16weeks. Empagliflozin administration increased UGE in the DIO mice, whereas it suppressed HFD-induced weight gain, insulin resistance, and hepatic steatosis. Moreover, empagliflozin shifted energy metabolism towards fat utilization, elevated AMP-activated protein kinase and acetyl-CoA carbolxylase phosphorylation in skeletal muscle, and increased hepatic and plasma fibroblast growth factor 21 levels. Importantly, empagliflozin increased energy expenditure, heat production, and the expression of uncoupling protein 1 in brown fat and in inguinal and epididymal white adipose tissue (WAT). Furthermore, empagliflozin reduced M1-polarized macrophage accumulation while inducing the anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype of macrophages within WAT and liver, lowering plasma TNFα levels and attenuating obesity-related chronic inflammation. Thus, empagliflozin suppressed weight gain by enhancing fat utilization and browning and attenuated obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance by polarizing M2 macrophages in WAT and liver.
Keywords: Brown adipose tissue; Energy metabolism; Inflammation; Macrophage; Obesity; Sodium glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Badman M.K., Pissios P., Kennedy A.R., Koukos G., Flier J.S., Maratos-Flier E. Hepatic fibroblast growth factor 21 is regulated by PPARalpha and is a key mediator of hepatic lipid metabolism in ketotic states. Cell Metab. 2007;5(6):426–437. - PubMed
-
- Bonner C., Kerr-Conte J., Gmyr V., Queniat G., Moerman E., Thevenet J., Beaucamps C., Delalleau N., Popescu I., Malaisse W.J. Inhibition of the glucose transporter SGLT2 with dapagliflozin in pancreatic alpha cells triggers glucagon secretion. Nat. Med. 2015;21(5):512–517. - PubMed
-
- Devenny J.J., Godonis H.E., Harvey S.J., Rooney S., Cullen M.J., Pelleymounter M.A. Weight loss induced by chronic dapagliflozin treatment is attenuated by compensatory hyperphagia in diet-induced obese (dio) rats. Obesity. 2012;20(8):1645–1652. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

