The role of ticks in the maintenance and transmission of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus: A review of published field and laboratory studies
- PMID: 28579441
- PMCID: PMC6047067
- DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2017.05.010
The role of ticks in the maintenance and transmission of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus: A review of published field and laboratory studies
Abstract
This manuscript is part of a series of reviews that aim to cover published research on Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever (CCHF) and its etiological agent, CCHF virus (CCHFV). The virus is maintained and transmitted in a vertical and horizontal transmission cycle involving a variety of wild and domestic vertebrate species that act as amplification hosts, without showing signs of illness. These vertebrates have traditionally been considered reservoirs of CCHFV, but in fact they develop only a transient viremia, while the virus can persist in ticks for their entire lifespan, and can also be transmitted vertically to the next generation. As a result, ticks are now considered to be both the vector and the reservoir for the virus. CCHFV has been detected in a wide range of tick species, but only a few have been proven to be vectors and reservoirs, mainly because most published studies have been performed under a broad variety of conditions, precluding definitive characterization. This article reviews the published literature, summarizes current knowledge of the role of ticks in CCHFV maintenance and transmission and provides guidance for how to fill the knowledge gaps. Special focus is given to existing data on tick species in which vertical passage has been demonstrated under natural or experimental conditions. At the same time, we identify earlier reports that used unreliable methods and perceptions to ascribe a vector role to some species of ticks, and have contributed to confusion regarding viral transmission. We also examine epidemiological pathways of CCHFV circulation and discuss priority areas for future research.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

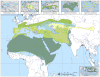
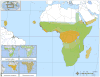
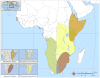
References
-
- Akuffo R, Brandful JAM, Zayed A, Adjei A, Watany N, Fahmy NT, Hughes R, Doman B, Voegborlo SV, Aziati D, Pratt D, Awuni JA, Adams N, Dueger E. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus in livestock ticks and animal handler seroprevalence at an abattoir in Ghana. BMC Infect Dis. 2016;16(1) - PMC - PubMed
-
- Albayrak H, Ozan E, Kurt M. Molecular detection of Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever virus (CCHFV) but not West Nile virus (WNV) in hard ticks from provinces in northern Turkey. Zoonoses Public Hlth. 2010a;57(7–8):156–160. - PubMed
-
- Albayrak H, Ozan E, Kurt M. An antigenic investigation of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus (CCHFV) in hard ticks from provinces in northern Turkey. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2010b;42(7):1323–1325. - PubMed
-
- Albayrak H, Ozan E, Kurt M. Serosurvey and molecular detection of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus (CCHFV) in northern Turkey. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2012;44(7):1667–1671. - PubMed
-
- Apanaskevich DA, Schuster AL, Horak IG. The genus Hyalomma: VII. Redescription of all parasitic stages of H (Euhyalomma) dromedarii and H (E.) schulzei (Acari: Ixodidae) J Med Entomol. 2008;45(5):817–831. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

