The Intergenerational Transmission of Union Instability in Early Adulthood
- PMID: 28579639
- PMCID: PMC5453673
- DOI: 10.1111/jomf.12384
The Intergenerational Transmission of Union Instability in Early Adulthood
Abstract
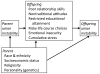
Research on the intergenerational transmission of divorce should be expanded to incorporate disrupted nonmarital cohabitations. The current study (1) examined the transmission of union instability from parents to offspring using Waves I and IV of Add Health, (2) replaced the binary variables (divorced versus non-divorced) typically used in this literature with count variables (number of disrupted unions), (3) relied on independent sources for data on parents' and offspring's union disruptions to minimize same-source bias, (4) assessed the mediating role of 11 theoretically derived variables (many not previously considered in this literature), and (5) incorporated information on discord in intact parental unions. Parent and offspring union disruptions were positively linked, with each parental disruption associated with a 16% increase in the number of offspring disruptions, net of controls. The mediators collectively accounted for 44% of the estimated intergenerational effect. Parent discord in intact unions also was associated with more offspring disruptions.
Keywords: couple relationships; dissolution; divorce; intergenerational issues; young adults.
Figures
References
-
- Amato PR. Consequences of divorce for adults and children. Journal of Marriage and the Family. 2000;62:1269–1287.
-
- Amato PR, DeBoer D. The transmission of divorce across generations: Relationship skills or commitment to marriage? Journal of Marriage and Family. 2001;63:1038–1051.
-
- Amato PR, Booth A. A generation at risk: Growing up in an era of family upheaval. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press; 1997.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources