Combination of Encephalo-Myo-Pial-Synangiosis and Encephalo-Arterio-Pial-Synangiosis Procedure in Pediatric Moya-Moya Disease
- PMID: 28579715
- PMCID: PMC5440834
- DOI: 10.4314/ejhs.v27i2.12
Combination of Encephalo-Myo-Pial-Synangiosis and Encephalo-Arterio-Pial-Synangiosis Procedure in Pediatric Moya-Moya Disease
Abstract
Background: Moya-moya disease in children is a cerebrovascular disorder that may cause cerebral ischemic or hemorrhage.
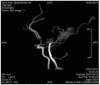
Case details: We report an 8-year-old boy that was admitted with the chief complaint of repeated sudden half left body paralyze. MRA showed acute thrombotic infarction in the right hemisphere and internal carotid artery stenosis in the form of puffs of smokes. Indirect revascularization surgical procedure with combination of Encephalo-myo-pial-synangiosis (EMS) and Encephalo-arterio-pial-synangiosis (EAS) was performed. It resulted in a good response.
Conclusion: Moya-moya disease can lead to permanent neurological disability if untreated. Satisfactory outcome was noted following combination surgery management with EMS and EAS.
Keywords: Encephalo-arterio-pial-synangiosis; Encephalo-myo-pial-synangiosis; Moya-moya disease; children.
Figures
References
-
- Smith JL. Understanding and treating moyamoya disease in children. Neurosurg focus. 2009;26:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Scott RM, Smith ER. Moyamoya disease and moyamoya syndrome. NEJM. 2009;360:1226–1237. - PubMed
-
- Baaj AA, Agazzi S, Sayed ZA, Toledo M, Spetzler RF, van Loveren H. Surgical management of moyamoya disease: a review. Neurosurg focus. 2009;26:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Achrol AS, Guzman R, Lee M, Steinberg GK. Pathophysiology and genetic factors in moyamoya disease. Neurosurg focus. 2009;26:1–6. - PubMed
-
- Janda PH, Bellew JG, Veerappan V. Moyamoya disease: case report and literature review. JAOA. 2009;109:547–553. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources