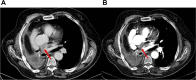
Extraordinary and prolonged erlotinib-induced clinical response in a patient with EGFR wild-type squamous lung cancer in third-line therapy: a case report
- PMID: 28579838
- PMCID: PMC5449169
- DOI: 10.2147/IMCRJ.S134944
Extraordinary and prolonged erlotinib-induced clinical response in a patient with EGFR wild-type squamous lung cancer in third-line therapy: a case report
Abstract
Several small molecules, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs), such as gefitinib, erlotinib and afatinib, have been demonstrated to significantly improve clinical outcomes in patients with advanced EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), but erlotinib activity in EGFR wild-type squamous carcinoma is still highly debated. Here, we describe a prolonged and unexpected clinical response to erlotinib in a male former heavy cigarette smoker with wild-type EGFR squamous-cell cancer.
Keywords: EGFR wild type; erlotinib; squamous NSCLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicenter, open-label, randomised phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13(3):239–246. - PubMed
-
- Shepherd FA, Rodrigues Pereira J, Ciuleanu T, et al. National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. Erlotinib in previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(2):123–132. - PubMed
-
- Cappuzzo F, Ciuleanu T, Stelmakh L, et al. Erlotinib as maintenance treatment in advanced non-small-cell-cancer: a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11(6):521–529. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous