Imaging Findings of Ulceroglandular Tularemia
- PMID: 28580063
- PMCID: PMC5443626
- DOI: 10.3941/jrcr.v11i1.2983
Imaging Findings of Ulceroglandular Tularemia
Abstract
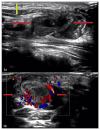
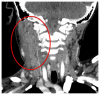
Francisella tularensis, the causative organism in Tularemia, is a relatively rare disease. There are a few radiological clues to elucidate its presence when suspicion arises. There should be strong consideration for Tularemia in the differential of any patient with its classic symptoms, diffuse cervical lymphadenopathy with evidence of necrosis, and enlarged adenoids. Ultrasound may demonstrate suppurative lymphadenopathy suggestive of infection, as in the case presented. CT often will demonstrate the extent of lymphadenopathy. On chest radiography, tularemia pneumonia is often the presenting finding, which may demonstrate bilateral or lobar infiltrates. Additionally, hilar lymphadenopathy and pleural effusions are often associated findings. Cavitary lesions may be present, which are better delineated on CT scan. We present a case of a 7-year-old male who presented with a painful right-sided palpable neck mass for 9 days, who was diagnosed with Tularemia after numerous admissions.
Keywords: Computer Tomography; Francisella; Lymphadenopathy; Rabbits; Suppurative; Tularemia; Tularensis; Ulceroglandular; Ultrasound.
Figures

References
-
- Baggett M, Gonzalez G, Bhattacharyya R, et al. Case 4-2016. New England Journal of Medicine. 2016;374(6):573–581. - PubMed
-
- Treat J, Hess S, McGowan K, Yan A, Kovarik C. Ulceroglandular Tularemia. Pediatric Dermatology. 2010;28(3):318–320. - PubMed
-
- Umlas S, Jaramillo D. Massive adenopathy in oropharyngeal tularemia; C. T. demonstration. Pediatric Radiology. 1990;20(6):483–484. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical