The prognostic value of procalcitonin, C-reactive protein and cholesterol in patients with an infection and multiple organ dysfunction
- PMID: 28580081
- PMCID: PMC5453892
- DOI: 10.4097/kjae.2017.70.3.305
The prognostic value of procalcitonin, C-reactive protein and cholesterol in patients with an infection and multiple organ dysfunction
Abstract
Background: To establish the prognostic value of procalcitonin, C-reactive protein and cholesterol levels for mortality in patients with an infection and multiple organ dysfunction.
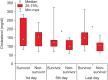
Methods: A prospective case-control study was performed, including 67 patients admitted to the intensive care unit with an infection and multiple organ dysfunction in whom cholesterol, procalcitonin, and C-reactive protein levels were measured on admission and during the course of treatment.
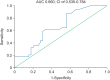
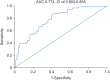
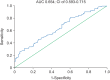
Results: The associations between in-hospital mortality and procalcitonin, C-reactive protein, and cholesterol levels were analyzed. Logistic regression analysis showed that cholesterol (odds ratio [OR], 1.858; 95% CI, 1.170-2.949; P = 0.009) and C-reactive protein (OR, 4.408; 95% CI, 2.019-9.624; P < 0.001) levels were predictors of mortality. A receiver operating characteristic curve analysis yielded an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.774 and 95% CI of 0.693-0.855 (P < 0.001) for C-reactive protein, an AUC of 0.66 and 95% CI of 0.535-0.784 (P = 0.019) for procalcitonin, and an AUC of 0.654 and 95% CI of 0.593-0.715 (P < 0.001) for cholesterol as predictors of mortality. When combined with the bioscore system for mortality, these markers yielded an AUC of 0.845 and 95% CI of 0.770-0.921 (P < 0.001), with sensitivity of 89.1% and specificity of 83.1%.
Conclusions: The combination of procalcitonin, C-reactive protein, and cholesterol levels in a single scoring system yielded high predictive value for mortality.
Keywords: C-reactive protein; Cholesterol; Infection; Mortality; Multiple organ dysfunction; Procalcitonin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diagnostic efficacy and prognostic value of serum procalcitonin concentration in patients with suspected sepsis.J Intensive Care Med. 2009 Jan-Feb;24(1):63-71. doi: 10.1177/0885066608327095. Epub 2008 Dec 2. J Intensive Care Med. 2009. PMID: 19054806 Clinical Trial.
-
C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, clinical pulmonary infection score, and pneumonia severity scores in nursing home acquired pneumonia.Respir Care. 2014 Apr;59(4):574-81. doi: 10.4187/respcare.02741. Epub 2013 Oct 8. Respir Care. 2014. PMID: 24106319
-
The utility of proadrenomedullin and procalcitonin in comparison to C-reactive protein as predictors of sepsis and bloodstream infections in critically ill patients with cancer*.Crit Care Med. 2014 Dec;42(12):2500-7. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000000526. Crit Care Med. 2014. PMID: 25083975
-
Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein as markers of bacterial infection in critically ill children at onset of systemic inflammatory response syndrome.Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2008 Jul;9(4):407-13. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0b013e31817285a6. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2008. PMID: 18496408
-
Prognostic value of procalcitonin in respiratory tract infections across clinical settings.Crit Care. 2015 Mar 6;19(1):74. doi: 10.1186/s13054-015-0792-1. Crit Care. 2015. PMID: 25887979 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Predicative values of C-reactive protein for the therapeutic effects of ulinastatin combined with somatostatin in severe acute pancreatitis and for the severity of gastrointestinal failure.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Oct;16(4):3165-3171. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6577. Epub 2018 Aug 7. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 30233671 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of lipid profile in adult hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis.Front Oncol. 2023 Feb 21;13:1083088. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1083088. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36895490 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of parameters in routine blood and coagulation tests related to the severity of COVID-19.Int J Med Sci. 2021 Jan 14;18(5):1207-1215. doi: 10.7150/ijms.47494. eCollection 2021. Int J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33526982 Free PMC article.
-
A new logistic regression model for early prediction of severity of acute pancreatitis using magnetic resonance imaging and Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II scoring systems.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2022 Sep;12(9):4424-4434. doi: 10.21037/qims-22-158. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2022. PMID: 36060575 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid Profile as a Predictive Marker for Organ Dysfunction after Thoracoabdominal Surgery: A Cross-sectional Study.Iran J Med Sci. 2023 Sep;48(5):465-473. doi: 10.30476/IJMS.2022.95364.2672. Iran J Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37786464 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mancini N, Burioni R, Clementi M. Microbiological diagnosis of sepsis: the confounding effects of a “gold standard”. Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1237:1–4. - PubMed
-
- Andrade SS, Bispo PJ, Gales AC. Advances in the microbiological diagnosis of sepsis. Shock. 2008;30(Suppl 1):41–46. - PubMed
-
- Luo XP, Wang HH, Hu SF, Wu SJ, Xie GH, Cheng BL, et al. Comparison of three different organ failure assessment score systems in predicting outcome of severe sepsis. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2009;47:48–50. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

