Genetic influences on individual differences in longitudinal changes in global and subcortical brain volumes: Results of the ENIGMA plasticity working group
- PMID: 28580697
- PMCID: PMC5572837
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.23672
Genetic influences on individual differences in longitudinal changes in global and subcortical brain volumes: Results of the ENIGMA plasticity working group
Abstract
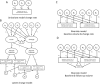
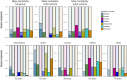
Structural brain changes that occur during development and ageing are related to mental health and general cognitive functioning. Individuals differ in the extent to which their brain volumes change over time, but whether these differences can be attributed to differences in their genotypes has not been widely studied. Here we estimate heritability (h2 ) of changes in global and subcortical brain volumes in five longitudinal twin cohorts from across the world and in different stages of the lifespan (N = 861). Heritability estimates of brain changes were significant and ranged from 16% (caudate) to 42% (cerebellar gray matter) for all global and most subcortical volumes (with the exception of thalamus and pallidum). Heritability estimates of change rates were generally higher in adults than in children suggesting an increasing influence of genetic factors explaining individual differences in brain structural changes with age. In children, environmental influences in part explained individual differences in developmental changes in brain structure. Multivariate genetic modeling showed that genetic influences of change rates and baseline volume significantly overlapped for many structures. The genetic influences explaining individual differences in the change rate for cerebellum, cerebellar gray matter and lateral ventricles were independent of the genetic influences explaining differences in their baseline volumes. These results imply the existence of genetic variants that are specific for brain plasticity, rather than brain volume itself. Identifying these genes may increase our understanding of brain development and ageing and possibly have implications for diseases that are characterized by deviant developmental trajectories of brain structure. Hum Brain Mapp 38:4444-4458, 2017. © 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Keywords: ENIGMA plasticity working group; heritability; individual brain plasticity; longitudinal magnetic resonance imaging; twins.
© 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Baare WF, Hulshoff Pol HE, Boomsma DI, Posthuma D, de Geus EJC, Schnack HG, van Haren NEM, van Oel CJ, Kahn RS (2001): Quantitative genetic modeling of variation in human brain morphology. Cereb Cortex 11:816–824. - PubMed
-
- Batouli SA, Trollor JN, Wen W, Sachdev PS (2014b): The heritability of volumes of brain structures and its relationship to age: A review of twin and family studies. Ageing Res Rev 13:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Bis JC, DeCarli C, Smith AV, van der Lijn F, Crivello F, Fornage M, Debette S, Shulman JM, Schmidt H, Srikanth V, Schuur M, Yu L, Choi SH, Sigurdsson S, Verhaaren BF, DeStefano AL, Lambert JC, Jack CR Jr, Struchalin M, Stankovich J, Ibrahim‐Verbaas CA, Fleischman D, Zijdenbos A, den Heijer T, Mazoyer B, Coker LH, Enzinger C, Danoy P, Amin N, Arfanakis K, van Buchem MA, de Bruijn RF, Beiser A, Dufouil C, Huang J, Cavalieri M, Thomson R, Niessen WJ, Chibnik LB, Gislason GK, Hofman A, Pikula A, Amouyel P, Freeman KB, Phan TG, Oostra BA, Stein JL, Medland SE, Vasquez AA, Hibar DP, Wright MJ, Franke B, Martin NG, Thompson PM; Enhancing Neuro Imaging Genetics through Meta‐Analysis Consortium , Nalls MA, Uitterlinden AG, Au R, Elbaz A, Beare RJ, van Swieten JC, Lopez OL, Harris TB, Chouraki V, Breteler MM, De Jager PL, Becker JT, Vernooij MW, Knopman D, Fazekas F, Wolf PA, van der Lugt A, Gudnason V, Longstreth WT Jr, Brown MA, Bennett DA, van Duijn CM, Mosley TH, Schmidt R, Tzourio C, Launer LJ, Ikram MA, Seshadri S; Cohorts for Heart and Aging Research in Genomic Epidemiology Consortium (2012): Common variants at 12q14 and 12q24 are associated with hippocampal volume. Nat Genet 44:545–551. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P41 EB015922/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG041915/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG022982/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG040060/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG018384/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U54 EB020403/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH089722/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH085667/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH094343/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG024904/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG024904/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 230374/ERC_/European Research Council/International
- R01 HD050735/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB008432/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS080655/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH097268/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG022381/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG050595/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

