Crystal structure of N-acetylmannosamine kinase from Fusobacterium nucleatum
- PMID: 28580924
- PMCID: PMC5458393
- DOI: 10.1107/S2053230X17007439
Crystal structure of N-acetylmannosamine kinase from Fusobacterium nucleatum
Abstract
Sialic acids comprise a varied group of nine-carbon amino sugars that are widely distributed among mammals and higher metazoans. Some human commensals and bacterial pathogens can scavenge sialic acids from their environment and degrade them for use as a carbon and nitrogen source. The enzyme N-acetylmannosamine kinase (NanK; EC 2.7.1.60) belongs to the transcriptional repressors, uncharacterized open reading frames and sugar kinases (ROK) superfamily. NanK catalyzes the second step of the sialic acid catabolic pathway, transferring a phosphate group from adenosine 5'-triphosphate to the C6 position of N-acetylmannosamine to generate N-acetylmannosamine 6-phosphate. The structure of NanK from Fusobacterium nucleatum was determined to 2.23 Å resolution by X-ray crystallography. Unlike other NanK enzymes and ROK family members, F. nucleatum NanK does not have a conserved zinc-binding site. In spite of the absence of the zinc-binding site, all of the major structural features of enzymatic activity are conserved.
Keywords: Fusobacterium nucleatum; N-acetylmannosamine kinase; sialic acid catabolism.
Figures


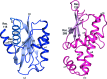

Similar articles
-
The basis for non-canonical ROK family function in the N-acetylmannosamine kinase from the pathogen Staphylococcus aureus.J Biol Chem. 2020 Mar 6;295(10):3301-3315. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.010526. Epub 2020 Jan 15. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 31949045 Free PMC article.
-
Structural studies on Mycobacterium tuberculosis HddA enzyme using small angle X-ray scattering and dynamics simulation techniques.Int J Biol Macromol. 2021 Feb 28;171:28-36. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.12.191. Epub 2021 Jan 5. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021. PMID: 33412198
-
Crystal structure of recombinant phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase 2 from Thermus thermophilus HB27 complexed with ADP and sulfate ions.Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2017 Jun 1;73(Pt 6):369-375. doi: 10.1107/S2053230X17007488. Epub 2017 May 31. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2017. PMID: 28580926 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of an ancestral ADP-dependent kinase with fructose-6P reveals key residues for binding, catalysis, and ligand-induced conformational changes.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100219. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015376. Epub 2020 Dec 24. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33839685 Free PMC article.
-
Catalytic and structural properties of ATP-dependent caprolactamase from Pseudomonas jessenii.Proteins. 2021 Sep;89(9):1079-1098. doi: 10.1002/prot.26082. Epub 2021 May 6. Proteins. 2021. PMID: 33826169 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Glycan cross-feeding supports mutualism between Fusobacterium and the vaginal microbiota.PLoS Biol. 2020 Aug 25;18(8):e3000788. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000788. eCollection 2020 Aug. PLoS Biol. 2020. PMID: 32841232 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and Function of N-Acetylmannosamine Kinases from Pathogenic Bacteria.ACS Omega. 2020 Nov 23;5(48):30923-30936. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.0c03699. eCollection 2020 Dec 8. ACS Omega. 2020. PMID: 33324800 Free PMC article.
-
Sugar-sensing swodkoreceptors and swodkocrine signaling.Animal Model Exp Med. 2025 May;8(5):944-961. doi: 10.1002/ame2.70007. Epub 2025 Mar 20. Animal Model Exp Med. 2025. PMID: 40110750 Free PMC article.
-
The basis for non-canonical ROK family function in the N-acetylmannosamine kinase from the pathogen Staphylococcus aureus.J Biol Chem. 2020 Mar 6;295(10):3301-3315. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.010526. Epub 2020 Jan 15. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 31949045 Free PMC article.
-
"Just a spoonful of sugar...": import of sialic acid across bacterial cell membranes.Biophys Rev. 2018 Apr;10(2):219-227. doi: 10.1007/s12551-017-0343-x. Epub 2017 Dec 8. Biophys Rev. 2018. PMID: 29222808 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

