The non-canonical NF-κB pathway in immunity and inflammation
- PMID: 28580957
- PMCID: PMC5753586
- DOI: 10.1038/nri.2017.52
The non-canonical NF-κB pathway in immunity and inflammation
Abstract
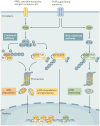
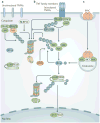
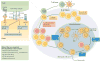
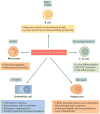
The nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) family of transcription factors is activated by canonical and non-canonical signalling pathways, which differ in both signalling components and biological functions. Recent studies have revealed important roles for the non-canonical NF-κB pathway in regulating different aspects of immune functions. Defects in non-canonical NF-κB signalling are associated with severe immune deficiencies, whereas dysregulated activation of this pathway contributes to the pathogenesis of various autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Here we review the signalling mechanisms and the biological function of the non-canonical NF-κB pathway. We also discuss recent progress in elucidating the molecular mechanisms regulating non-canonical NF-κB pathway activation, which may provide new opportunities for therapeutic strategies.
Figures

References
-
- Hayden MS, Ghosh S. Shared principles in NF-κB signaling. Cell. 2008;132:344–362. - PubMed
-
- Lin L, DeMartino GN, Greene WC. Cotranslational biogenesis of NF-κB p50 by the 26S proteasome. Cell. 1998;92:819–828. - PubMed
-
- Vallabhapurapu S, Karin M. Regulation and function of NF-κB transcription factors in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 2009;27:693–733. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

