The extracellular matrix protein agrin promotes heart regeneration in mice
- PMID: 28581497
- PMCID: PMC5769930
- DOI: 10.1038/nature22978
The extracellular matrix protein agrin promotes heart regeneration in mice
Abstract
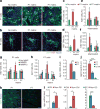
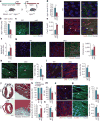
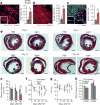
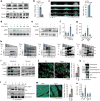
The adult mammalian heart is non-regenerative owing to the post-mitotic nature of cardiomyocytes. The neonatal mouse heart can regenerate, but only during the first week of life. Here we show that changes in the composition of the extracellular matrix during this week can affect cardiomyocyte growth and differentiation in mice. We identify agrin, a component of neonatal extracellular matrix, as required for the full regenerative capacity of neonatal mouse hearts. In vitro, recombinant agrin promotes the division of cardiomyocytes that are derived from mouse and human induced pluripotent stem cells through a mechanism that involves the disassembly of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex, and Yap- and ERK-mediated signalling. In vivo, a single administration of agrin promotes cardiac regeneration in adult mice after myocardial infarction, although the degree of cardiomyocyte proliferation observed in this model suggests that there are additional therapeutic mechanisms. Together, our results uncover a new inducer of mammalian heart regeneration and highlight fundamental roles of the extracellular matrix in cardiac repair.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
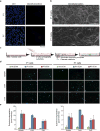
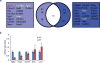

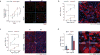
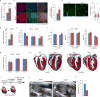
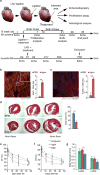
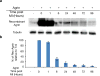
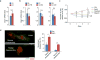
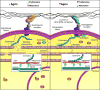
Comment in
-
Heart Regeneration 4.0: Matrix Medicine.Dev Cell. 2017 Jul 10;42(1):7-8. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2017.06.017. Dev Cell. 2017. PMID: 28697334
References
-
- Soonpaa MH, Kim KK, Pajak L, Franklin M, Field LJ. Cardiomyocyte DNA synthesis and binucleation during murine development. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 1996;271:H2183–H2189. - PubMed
-
- Rupp F, Payan DG, Magill-Solc C, Cowan DM, Scheller RH. Structure and expression of a rat agrin. Neuron. 1991;6:811–823. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

