Racial/ethnic disparities in the prevalence and awareness of Hepatitis B virus infection and immunity in the United States
- PMID: 28581638
- PMCID: PMC5638673
- DOI: 10.1111/jvh.12735
Racial/ethnic disparities in the prevalence and awareness of Hepatitis B virus infection and immunity in the United States
Abstract
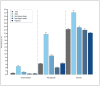
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection in the United States is the most common among Asians followed by non-Hispanic blacks. However, there have been few studies that describe HBV infection and immunity by racial group. Our study aimed to assess racial/ethnic disparities in the prevalence and awareness of HBV infection and immunity using nationally representative data. In the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011-2014, 14 722 persons had HBV serology testing. We estimated the prevalence of HBV infection, past exposure, and immunity by selected characteristics and calculated adjusted odds ratios using survey-weighted generalized logistic regression. Awareness of infection and vaccination history was also investigated. The overall prevalence of chronic HBV infection, past exposure and vaccine-induced immunity was 0.34% [95%CI 0.24-0.43], 4.30% [95%CI 3.80-4.81], and 24.4% [95%CI 23.4-25.4], respectively. The prevalence of chronic infection was 2.74% [95% CI 1.72-3.76] in Asians, 0.64% [95% CI 0.35-0.92] in non-Hispanic blacks, and 0.15% [95% CI 0.06-0.24] in non-Asian, non-blacks. Only 26.2% of those with chronic infection were aware of their infection. The prevalence of the past exposure was 21.5% [95%CI 19.3-23.7] in Asians, 8.92% [95%CI 7.84-9.99] in non-Hispanic blacks, 2.05% [95%CI 1.49-2.63] in non-Hispanic whites and 4.47% [95%CI 3.25-5.70] in Hispanics. Prevalence of vaccine-induced immunity by each race was 34.1% [95%CI: 32.0-36.2] in Asians, 25.5% [95%CI: 24.0-27.0] in non-Hispanic blacks, 24.0% [95%CI: 22.6-25.4] in non-Hispanic whites and 22.2% [95%CI: 21.3-23.3] in Hispanics. There are considerable racial/ethnic disparities in HBV infection, exposure and immunity. More active and sophisticated healthcare policies on HBV management may be warranted.
Keywords: Hepatitis B virus; National Health Nutrition Examination Survey; awareness; epidemiology; racial disparity.
© 2017 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: nothing to disclose
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hepatitis B virus in the United States: infection, exposure, and immunity rates in a nationally representative survey.Ann Intern Med. 2011 Mar 1;154(5):319-28. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-154-5-201103010-00006. Ann Intern Med. 2011. PMID: 21357909
-
Prevalence of HBV Infection, Vaccine-Induced Immunity, and Susceptibility Among At-Risk Populations: US Households, 2013-2018.Hepatology. 2021 Nov;74(5):2353-2365. doi: 10.1002/hep.31991. Epub 2021 Jul 13. Hepatology. 2021. PMID: 34097776
-
Hepatitis B virus infection and immunizations among Asian American college students: infection, exposure, and immunity rates.J Am Coll Health. 2013;61(2):67-74. doi: 10.1080/07448481.2012.753891. J Am Coll Health. 2013. PMID: 23409856
-
Prevalence of Undetectable Vaccine-Induced Immunity Against Hepatitis B Virus in US Adults at High Risk for Infection.Hepatology. 2019 Apr;69(4):1385-1397. doi: 10.1002/hep.30285. Epub 2019 Feb 20. Hepatology. 2019. PMID: 30246260
-
Expression and detection of anti-HBs antibodies after hepatitis B virus infection or vaccination in the context of protective immunity.Arch Virol. 2019 Nov;164(11):2645-2658. doi: 10.1007/s00705-019-04369-9. Epub 2019 Aug 9. Arch Virol. 2019. PMID: 31399876 Review.
Cited by
-
An examination of factors associated with disparities in clinical trial eligibility guided by the Socioecological Model.Cancer. 2025 Jul 1;131(13):e35944. doi: 10.1002/cncr.35944. Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40530674 Free PMC article.
-
Disparities in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Incidence, Stage, and Survival: A Large Population-Based Study.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2021 Jun;30(6):1193-1199. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-20-1088. Epub 2021 Mar 18. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2021. PMID: 33737301 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in Hepatitis B Infection and Immunity Among Women of Childbearing Age in the United States.Clin Infect Dis. 2020 Jul 27;71(3):586-592. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciz841. Clin Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 31504302 Free PMC article.
-
Implementing Adult Hepatitis B Immunization and Screening Using Electronic Health Records: A Practical Guide.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 May 14;12(5):536. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12050536. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38793787 Free PMC article.
-
Testing for hepatitis B virus alone does not increase vaccine coverage in non-immunized persons.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Oct 14;23(38):7037-7046. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i38.7037. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 29097876 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Buckley GJ, Strom BL. What Stands in the Way of Making Hepatitis B and C Rare Diseases in the United States? Ann Intern Med. 2016;165(4):284–285. - PubMed
-
- Roberts H, Kruszon-Moran D, Ly KN, et al. Prevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection in U.S. households: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), 1988–2012. Hepatology. 2016;63(2):388–397. - PubMed
-
- Weinbaum CM, Williams I, Mast EE, et al. Recommendations for identification and public health management of persons with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2008;57(RR-8):1–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous