Arsenic affects inflammatory cytokine expression in Gallus gallus brain tissues
- PMID: 28583123
- PMCID: PMC5460324
- DOI: 10.1186/s12917-017-1066-8
Arsenic affects inflammatory cytokine expression in Gallus gallus brain tissues
Abstract
Background: The heavy metal arsenic is widely distributed in nature and posses a serious threat to organism's health. However, little is known about the arsenic-induced inflammatory response in the brain tissues of birds and the relationship and mechanism of the inflammatory response. The purpose of this study was to explore the effects of dietary arsenic on the expression of inflammatory cytokines in the brains of Gallus gallus.
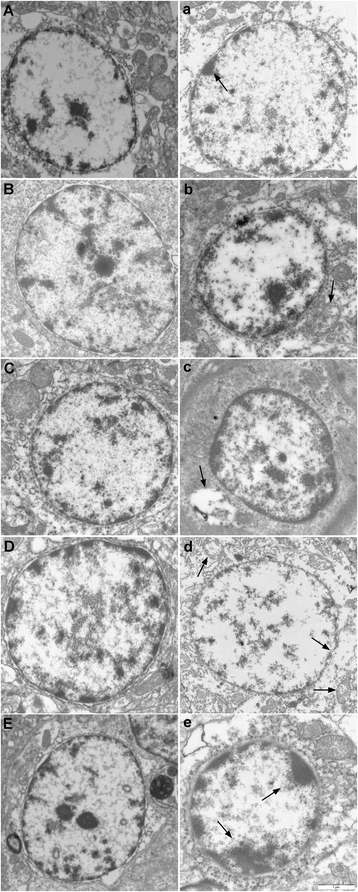
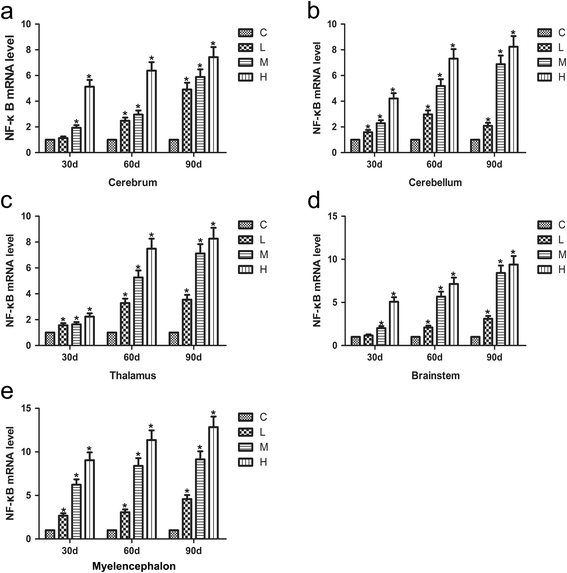
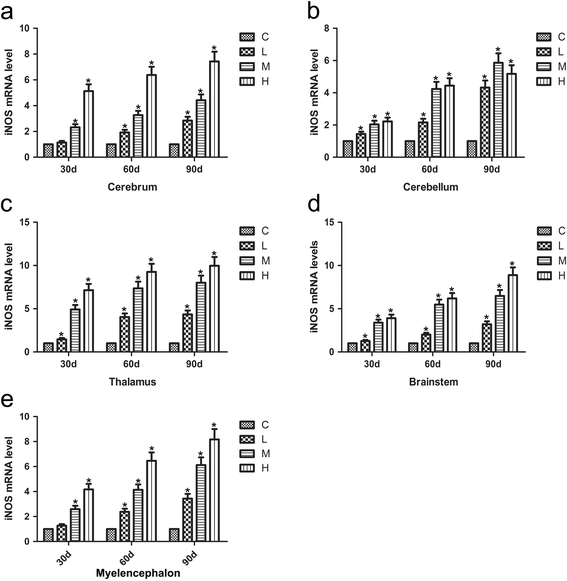
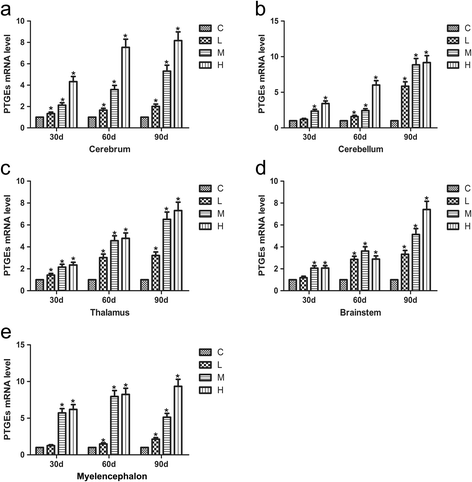
Results: Seventy-two 1-day-old male Hy-line chickens were divided into a control group, a low arsenic trioxide (As2O3)-treated (7.5 mg/kg) group, a middle As2O3-treated (15 mg/kg) group, and a high As2O3-treated (30 mg/kg) group. Arsenic exposure caused obvious ultrastructural changes. The mRNA levels of the transcription factor nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including inducible NO synthase (iNOS), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), and prostaglandin E synthase (PTGEs), in chicken brain tissues (cerebrum, cerebellum, thalamus, brainstem and myelencephalon) on days 30, 60 and 90, respectively, were measured by real-time PCR. The protein expression of iNOS was detected by western blot. The results showed that after being treated with As2O3, the levels of inflammatory-related factor NF-κB and pro-inflammatory cytokines in chicken brain tissues increased (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: Arsenic exposure in the chickens triggered host defence and induced an inflammatory response by regulating the expression of inflammatory-related genes in the cerebrum, cerebellum, thalamus, brainstem and myelencephalon. These data form a foundation for further research on arsenic-induced neurotoxicity in Gallus gallus.
Keywords: Arsenic; Brain tissues; Chickens; Inflammatory cytokines; NF-κB.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Assessment of arsenic trioxide in the heart of Gallus gallus: alterations of oxidative damage parameters, inflammatory cytokines, and cardiac enzymes.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017 Feb;24(6):5781-5790. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-8223-7. Epub 2017 Jan 4. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28054265
-
NF-κB-mediated inflammation correlates with calcium overload under arsenic trioxide-induced myocardial damage in Gallus gallus.Chemosphere. 2017 Oct;185:618-627. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.07.055. Epub 2017 Jul 14. Chemosphere. 2017. PMID: 28728119
-
Synergistic effect of copper and arsenic upon oxidative stress, inflammation and autophagy alterations in brain tissues of Gallus gallus.J Inorg Biochem. 2018 Jan;178:54-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2017.10.006. Epub 2017 Oct 12. J Inorg Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29054015
-
Arsenic and/or copper caused inflammatory response via activation of inducible nitric oxide synthase pathway and triggered heat shock protein responses in testis tissues of chicken.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018 Mar;25(8):7719-7729. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-1042-7. Epub 2017 Dec 29. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29288301
-
Arsenic Trioxide Attenuates NF-κB and Cytokine mRNA Levels in the Livers of Cocks.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2016 Apr;170(2):432-7. doi: 10.1007/s12011-015-0455-8. Epub 2015 Aug 16. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2016. PMID: 26276563
Cited by
-
Recapitulation of Structure-Function-Regulation of Blood-Brain Barrier under (Patho)Physiological Conditions.Cells. 2024 Jan 30;13(3):260. doi: 10.3390/cells13030260. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38334652 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coenzyme Q10 protected against arsenite and enhanced the capacity of 2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid to ameliorate arsenite-induced toxicity in mice.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2021 Apr 7;22(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s40360-021-00484-z. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33827703 Free PMC article.
-
Redox Homeostasis in Poultry: Regulatory Roles of NF-κB.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Jan 28;10(2):186. doi: 10.3390/antiox10020186. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33525511 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of Metal-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Neurological Disorders.Toxics. 2021 Jun 17;9(6):142. doi: 10.3390/toxics9060142. Toxics. 2021. PMID: 34204190 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Selenium on Brain Injury in Chickens with Subacute Arsenic Poisoning.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2022 Jan;200(1):330-338. doi: 10.1007/s12011-021-02630-4. Epub 2021 Feb 16. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2022. PMID: 33594525
References
-
- Milton AH, Hasan Z, Rahman A. Chronic arsenic poisoning and respiratory effects in Bangladesh. J Occup Health. 2001;43:136–140. doi: 10.1539/joh.43.136. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

