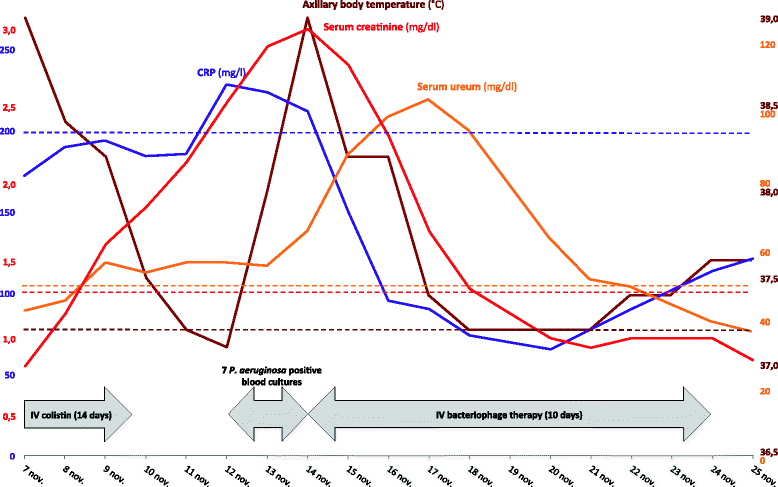
Use of bacteriophages in the treatment of colistin-only-sensitive Pseudomonas aeruginosa septicaemia in a patient with acute kidney injury-a case report
- PMID: 28583189
- PMCID: PMC5460490
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-017-1709-y
Use of bacteriophages in the treatment of colistin-only-sensitive Pseudomonas aeruginosa septicaemia in a patient with acute kidney injury-a case report
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Antibiotic resistance; Bacteraemia; Bacteriophage therapy; Colistin; Intravenous; Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources