A brief review: adipose-derived stem cells and their therapeutic potential in cardiovascular diseases
- PMID: 28583198
- PMCID: PMC5460549
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-017-0585-3
A brief review: adipose-derived stem cells and their therapeutic potential in cardiovascular diseases
Abstract
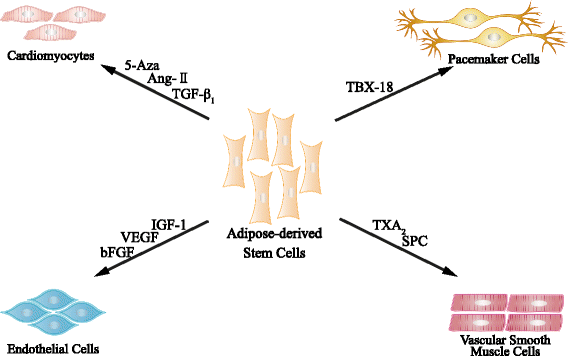
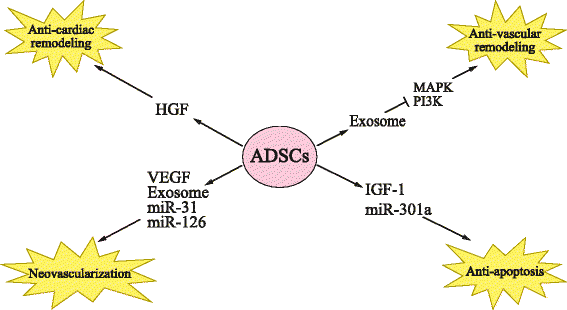
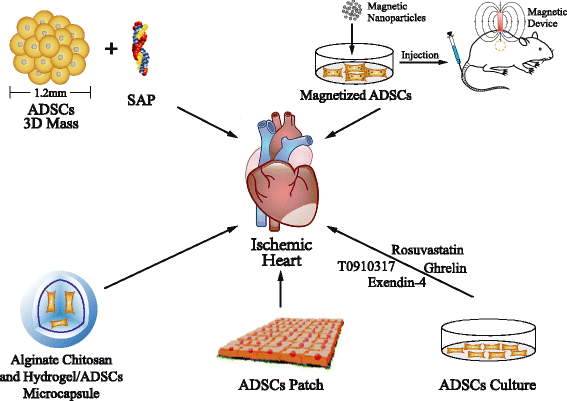
Adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) are easily obtained and expanded, and have emerged as a novel source of adult stem cells for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. These cells have been shown to have the capability of differentiating into cardiomyocytes, vascular smooth muscle cells, and endothelial cells. Furthermore, ADSCs secrete a series of paracrine factors to promote neovascularization, reduce apoptosis, and inhibit fibrosis, which contributes to cardiac regeneration. As a novel therapy in the regenerative field, ADSCs still face various limitations, such as low survival and engraftment. Thus, engineering and pharmacological studies have been conducted to solve these problems. Investigations have moved into phase I and II clinical trials examining the safety and efficacy of ADSCs in the setting of myocardial infarction. In this review, we discuss the differentiation and paracrine functions of ADSCs, the strategies promoting their therapeutic efficacy, and their clinical usage.
Keywords: Adipose-derived stem cells; Cardiovascular diseases; Differentiation; Paracrine effect; Stem cell transplantation.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

