Increased temporal discounting after chronic stress in CHL1-deficient mice is reversed by 5-HT2C agonist Ro 60-0175
- PMID: 28583411
- PMCID: PMC5546908
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.05.047
Increased temporal discounting after chronic stress in CHL1-deficient mice is reversed by 5-HT2C agonist Ro 60-0175
Abstract
Schizophrenia is a neurodevelopmental disorder in which impaired decision-making and goal-directed behaviors are core features. One of the genes associated with schizophrenia is the Close Homolog of L1 (CHL1); CHL1-deficient mice are considered a model of schizophrenia-like deficits, including sensorimotor gating, interval timing and spatial memory impairments. Here we investigated temporal discounting in CHL1-deficient (KO) mice and their wild-type littermates. Although no discounting differences were found under baseline conditions, CHL1-KO mice showed increased impulsive choice following chronic unpredictable stress (fewer % larger-later choices, and reduced area under the discounting curve). Stressed CHL1-KO mice also showed decreased neuronal activation (number of cFos positive neurons) in the discounting task in the prelimbic cortex and dorsal striatum, areas thought to be part of executive and temporal processing circuits. Impulsive choice alterations were reversed by the 5-HT2C agonist Ro 60-0175. Our results provide evidence for a gene x environment, double-hit model of stress-related decision-making impairments, and identify CHL1-deficient mice as a mouse model for these deficits in regard to schizophrenia-like phenotypes.
Keywords: cFos; intertemporal decision making; prefrontal cortex; schizophrenia; serotonin; striatum.
Copyright © 2017 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures
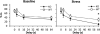
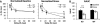
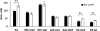
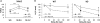
Similar articles
-
Chronic mild stress impairs latent inhibition and induces region-specific neural activation in CHL1-deficient mice, a mouse model of schizophrenia.Behav Brain Res. 2017 Aug 30;333:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2017.06.033. Epub 2017 Jun 21. Behav Brain Res. 2017. PMID: 28647594 Free PMC article.
-
Role of 5-HT2C receptors in the enhancement of c-Fos expression induced by a 5-HT2B/2C inverse agonist and 5-HT 2 agonists in the rat basal ganglia.Exp Brain Res. 2013 Oct;230(4):525-35. doi: 10.1007/s00221-013-3562-9. Epub 2013 May 17. Exp Brain Res. 2013. PMID: 23681297
-
Interaction between CHL1 and serotonin receptor 2c regulates signal transduction and behavior in mice.J Cell Sci. 2015 Dec 15;128(24):4642-52. doi: 10.1242/jcs.176941. Epub 2015 Nov 2. J Cell Sci. 2015. PMID: 26527397
-
Impaired interval timing and spatial-temporal integration in mice deficient in CHL1, a gene associated with schizophrenia.Timing Time Percept. 2013;1(1):21-38. doi: 10.1163/22134468-00002003. Timing Time Percept. 2013. PMID: 28890867 Free PMC article.
-
A meta-analytical review of brain activity associated with intertemporal decisions: Evidence for an anterior-posterior tangibility axis.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2018 Mar;86:85-98. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.01.005. Epub 2018 Feb 2. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2018. PMID: 29366699 Review.
Cited by
-
A Population-Based Model of the Temporal Memory in the Hippocampus.Front Neurosci. 2018 Aug 7;12:521. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00521. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30131668 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of chronic stress on cognitive function - From neurobiology to intervention.Neurobiol Stress. 2024 Sep 2;33:100670. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2024.100670. eCollection 2024 Nov. Neurobiol Stress. 2024. PMID: 39295772 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blockade of Catecholamine Reuptake in the Prelimbic Cortex Decreases Top-down Attentional Control in Response to Novel, but Not Familiar Appetitive Distracters, within a Timing Paradigm.NeuroSci. 2020 Dec;1(2):99-114. doi: 10.3390/neurosci1020010. Epub 2020 Dec 8. NeuroSci. 2020. PMID: 35036990 Free PMC article.
-
5-HT1a Receptor Involvement in Temporal Memory and the Response to Temporal Ambiguity.Front Neurosci. 2018 Jul 3;12:439. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00439. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30018532 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the Serotonergic System in Time Perception: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 11;25(24):13305. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413305. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769070 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adriani W, Laviola G. Elevated levels of impulsivity and reduced place conditioning with d-amphetamine: two behavioral features of adolescence in mice. Behav Neurosci. 2003;117:695–703. - PubMed
-
- Ahmad A, Rasheed N, Banu N, Palit G. Alterations in monoamine levels and oxidative systems in frontal cortex, striatum, and hippocampus of the rat brain during chronic unpredictable stress. Stress. 2010;13:355–364. - PubMed
-
- Aiello G, Horowitz M, Hepgul N, Pariante CM, Mondelli V. Stress abnormalities in individuals at risk for psychosis: a review of studies in subjects with familial risk or with "at risk" mental state. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2012;37:1600–1613. - PubMed
-
- Alex KD, Yavanian GJ, McFarlane HG, Pluto CP, Pehek EA. Modulation of dopamine release by striatal 5-HT2C receptors. Synapse. 2005;55:242–251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

