Cyp1b1 deletion and retinol deficiency coordinately suppress mouse liver lipogenic genes and hepcidin expression during post-natal development
- PMID: 28583802
- PMCID: PMC5985816
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mce.2017.05.037
Cyp1b1 deletion and retinol deficiency coordinately suppress mouse liver lipogenic genes and hepcidin expression during post-natal development
Abstract
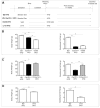
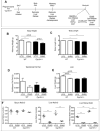
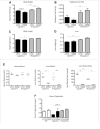
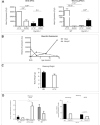
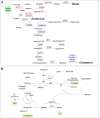
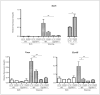
Cyp1b1 deletion and gestational vitamin A deficiency (GVAD) redirect adult liver gene expression. A matched sufficient pre- and post-natal diet, which has high carbohydrate and normal iron content (LF12), increased inflammatory gene expression markers in adult livers that were suppressed by GVAD and Cyp1b1 deletion. At birth on the LF12 diet, Cyp1b1 deletion and GVAD each suppress liver expression of the iron suppressor, hepcidin (Hepc), while increasing stellate cell activation markers and suppressing post-natal increases in lipogenesis. Hepc was less suppressed in Cyp1b1-/- pups with a standard breeder diet, but was restored by iron supplementation of the LF12 diet.
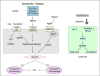
Conclusions: The LF12 diet delivered low post-natal iron and attenuated Hepc. Hepc decreases in Cyp1b1-/- and GVAD mice resulted in stellate activation and lipogenesis suppression. Endothelial BMP6, a Hepc stimulant, is a potential coordinator and Cyp1b1 target. These neonatal changes in Cyp1b1-/- mice link to diminished adult obesity and liver inflammation.
Keywords: Cytochrome P450 1b1; Hepcidin; Lipogenesis; Vitamin A; Vitamin A deficiency.
Copyright © 2017. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures
References
-
- Armitage AE, Eddowes LA, Gileadi U, Cole S, Spottiswoode N, Selvakumar TA, Ho LP, Townsend AR, Drakesmith H. Hepcidin regulation by innate immune and infectious stimuli. Blood. 2011;118:4129–39. - PubMed
-
- Arndt S, Wacker E, Dorn C, Koch A, Saugspier M, Thasler WE, Hartmann A, Bosserhoff AK, Hellerbrand C. Enhanced expression of BMP6 inhibits hepatic fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Gut. 2015;64:973–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

