The effect of the neutral cytidine protonated analogue pseudoisocytidine on the stability of i-motif structures
- PMID: 28584239
- PMCID: PMC5459817
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-02723-y
The effect of the neutral cytidine protonated analogue pseudoisocytidine on the stability of i-motif structures
Abstract
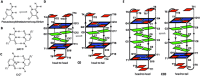
Incorporation of pseudoisocytidine (psC), a neutral analogue of protonated cytidine, in i-motifs has been studied by spectroscopic methods. Our results show that neutral psC:C base pairs can stabilize i-motifs at neutral pH, but the stabilization only occurs when psC:C base pairs are located at the ends of intercalated C:C+ stacks. When psC occupies central positions, the resulting i-motifs are only observed at low pH and psC:C+ or psC:psC+ hemiprotonated base pairs are formed instead of their neutral analogs. Overall, our results suggest that positively charged base pairs are necessary to stabilize this non-canonical DNA structure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Benabou S, Aviñó A, Eritja R, González C, Gargallo R. Fundamental aspects of the nucleic acid i-motif structures. RSC Adv. 2014;4:26956–52. doi: 10.1039/c4ra02129k. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

