Prediction of outcome in newly diagnosed myeloma: a meta-analysis of the molecular profiles of 1905 trial patients
- PMID: 28584253
- PMCID: PMC5590713
- DOI: 10.1038/leu.2017.179
Prediction of outcome in newly diagnosed myeloma: a meta-analysis of the molecular profiles of 1905 trial patients
Abstract
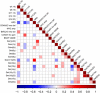
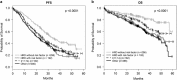
Robust establishment of survival in multiple myeloma (MM) and its relationship to recurrent genetic aberrations is required as outcomes are variable despite apparent similar staging. We assayed copy number alterations (CNA) and translocations in 1036 patients from the NCRI Myeloma XI trial and linked these to overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival. Through a meta-anlysis of these data with data from MRC Myeloma IX trial, totalling 1905 newly diagnosed MM patients (NDMM), we confirm the association of t(4;14), t(14;16), t(14;20), del(17p) and gain(1q21) with poor prognosis with hazard ratios (HRs) for OS of 1.60 (P=4.77 × 10-7), 1.74 (P=0.0005), 1.90 (P=0.0089), 2.10 (P=8.86 × 10-14) and 1.68 (P=2.18 × 10-14), respectively. Patients with 'double-hit' defined by co-occurrence of at least two adverse lesions have an especially poor prognosis with HRs for OS of 2.67 (P=8.13 × 10-27) for all patients and 3.19 (P=1.23 × 10-18) for intensively treated patients. Using comprehensive CNA and translocation profiling in Myeloma XI we also demonstrate a strong association between t(4;14) and BIRC2/BIRC3 deletion (P=8.7 × 10-15), including homozygous deletion. Finally, we define distinct sub-groups of hyperdiploid MM, with either gain(1q21) and CCND2 overexpression (P<0.0001) or gain(11q25) and CCND1 overexpression (P<0.0001). Profiling multiple genetic lesions can identify MM patients likely to relapse early allowing stratification of treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Honoraria from Novartis, Pfizer, Takeda, Janssen by EMB; research support from Celgene by JRJ; consultancy and honoraria from Celgene, Novartis, Takeda by CP; SS was employed by MRC Holland; Honoraria and consultancy from Janssen, Novartis, Amgen, Takeda, Celgene by MWJ; Research funding: Janssen, Celgene; employment, equity ownership, royalties from Abingdon Health/Serascience by MTD; honoraria, consultancy from Celgene, Takeda, Janssen by RGO; Research funding from Celgene by DAC; Research Funding from Celgene by WMG; consultancy and research funding from Janssen, Celgene, Takeda Oncology, Sanofi, Amgen and BMS by GC; honoraria from Takeda-Millenium, Onyx/Amgen, Celgene and Janssen by FED; GHJ: honoraria and consultancy from Celgene, Takeda, MSD, Janssen, Roche andAmgen; research funding and travel support from Celgene and Takeda; honoraria, consultancy, research funding from Celgene, Takeda-Millennium, BMS by GJM; honoraria from Amgen, Celgene, Janssen: Consultancy for Takeda, Amgen, Chugai Pharma, BMS, Janssen; Research Funding from Celgene by MFK. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Chng WJ, Dispenzieri A, Chim CS, Fonseca R, Goldschmidt H, Lentzsch S et al. IMWG consensus on risk stratification in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2013; 28: 269–277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

