Assessment of Perception, Experience, and Information-seeking Behavior of the Public of Ras Al-Khaimah, United Arab Emirates, Toward Usage and Safety of Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- PMID: 28584493
- PMCID: PMC5450470
- DOI: 10.4103/jpbs.JPBS_337_16
Assessment of Perception, Experience, and Information-seeking Behavior of the Public of Ras Al-Khaimah, United Arab Emirates, Toward Usage and Safety of Complementary and Alternative Medicine
Abstract
Aims and objectives: This study was conducted to identify the different types of complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) used, reasons for the use of CAM, and the perceptions, experience, and information seeking-behavior toward usage and safety of CAM by the general public of Ras Al-Khaimah, UAE.
Materials and methods: This was a prospective cross-sectional study. A validated, self-administered, or interviewer-assisted survey questionnaire was used to collect the data. Data from 403 respondents satisfying inclusion criteria were collected and were analyzed using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences version 24.0.
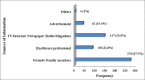
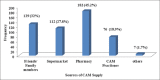
Results: A majority of the respondents (218 [54.1%]) were females. The most commonly (210 [52.1%]) used CAM among the study respondents was herbal medicine. A total of 91 (22.6%) of the survey respondents mentioned that they receive conventional medications along with their CAM. Majority (213 [52.9%]) of the survey respondents opted for CAM to prevent illness. Good number (208 [51.6%]) of the survey respondents mentioned that CAM usage was beneficial in improving their health condition, and they (216 [53.6%]) do believe it as safe and effective. However, a small group (26 [6%]) of respondents reported side effects or complications with the use of CAM.
Conclusion: Widespread use of CAM for different medical problems was evident in our study. Although majority of the CAM users believe it as safe and effective, CAM usage should be discussed with the health-care providers to understand the safety issues involved in the use of majority of CAM.
Keywords: Complementary and alternative medicine; experience; information-seeking behavior; perception.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Posadzki P, Lee MS, Moon TW, Choi TY, Park TY, Ernst E. Prevalence of complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) use by menopausal women: A systematic review of surveys. Maturitas. 2013;75:34–43. - PubMed
-
- National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine. The Use of Complementary and Alternative Medicine Use in the United States. [Last accessed on 2014 Oct 17]. Available from: http://www.nccam.nih.gov/sites/nccam.nih.gov/files/camuse.pdf .
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources