Stress distribution in maxillary first molar periodontium using straight pull headgear with vertical and horizontal tubes: A finite element analysis
- PMID: 28584535
- PMCID: PMC5443006
- DOI: 10.4103/1735-3327.205795
Stress distribution in maxillary first molar periodontium using straight pull headgear with vertical and horizontal tubes: A finite element analysis
Abstract
Background: One of the most effective ways for distal movement of molars to treat Class II malocclusion is using extraoral force through a headgear device. The purpose of this study was the comparison of stress distribution in maxillary first molar periodontium using straight pull headgear in vertical and horizontal tubes through finite element method.
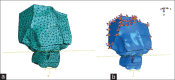
Materials and methods: Based on the real geometry model, a basic model of the first molar and maxillary bone was obtained using three-dimensional imaging of the skull. After the geometric modeling of periodontium components through CATIA software and the definition of mechanical properties and element classification, a force of 150 g for each headgear was defined in ABAQUS software. Consequently, Von Mises and Principal stresses were evaluated. The statistical analysis was performed using T-paired and Wilcoxon nonparametric tests.
Results: Extension of areas with Von Mises and Principal stresses utilizing straight pull headgear with a vertical tube was not different from that of using a horizontal tube, but the numerical value of the Von Mises stress in the vertical tube was significantly reduced (P < 0/05). On the other hand, the difference of the principal stress between both tubes was not significant (P > 0/05).
Conclusion: Based on the results, when force applied to the straight pull headgear with a vertical tube, Von Mises stress was reduced significantly in comparison with the horizontal tube. Therefore, to correct the mesiolingual movement of the maxillary first molar, vertical headgear tube is recommended.
Keywords: Dental stress analyses; Finite element analysis; extraoral traction appliance; maxilla; molar.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare that they have no conflicts of interest, real or perceived, financial or non-financial in this article.
Figures





References
-
- Pancherz H. Treatment of class II malocclusions by jumping the bite with the Herbst appliance. A cephalometric investigation. Am J Orthod. 1979;76:423–42. - PubMed
-
- Herrera-Sanches FS, Henriques JF, Janson G, Neves LS, de Lima KJ, Henriques RP, et al. Class II malocclusion treatment using Jasper Jumper appliance associated to intermaxillary elastics: A case report. Dental Press J Orthod. 2013;18:22–9. - PubMed
-
- Haydar S, Uner O. Comparison of Jones jig molar distalization appliance with extraoral traction. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2000;117:49–53. - PubMed
-
- Ghosh J, Nanda RS. Evaluation of an intraoral maxillary molar distalization technique. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1996;110:639–46. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
