Active Ingredients of Epimedii Folium and Ligustri Lucidi Fructus Balanced GR/HSP90 to Improve the Sensitivity of Asthmatic Rats to Budesonide
- PMID: 28584561
- PMCID: PMC5444006
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/7961231
Active Ingredients of Epimedii Folium and Ligustri Lucidi Fructus Balanced GR/HSP90 to Improve the Sensitivity of Asthmatic Rats to Budesonide
Abstract
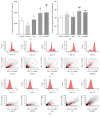
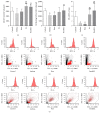
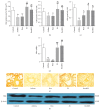
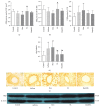
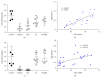
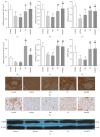
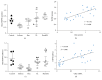
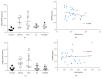
This study aimed to investigate the possible molecular mechanisms of active ingredients of Epimedii Folium (EF) and Ligustri Lucidi Fructus (LLF) combined with Budesonide (Bun) in asthmatic rats. Rats were divided into 5 groups, including normal group, asthma model group, Bun group, group of active ingredients of EL and LLF (EL), and group of coadministration of Bun with EL (Bun&EL). The asthmatic model was prepared by ovalbumin sensitizing and challenging. Lymphocyte apoptosis, GR protein and binding, and the protein and mRNA of GRα, GRβ, and HSP90 were tested. The results showed that Bun&EL ① markedly increased lymphocyte apoptosis, GR and HSP90 protein, and GR binding in BALF and ② enhanced the expressions of GRα and HSP90 and the ratio of GRα to GRβ or to HSP90 both in protein and in mRNA levels in lung, ③ while decrease occurred in GRβ mRNA and the mRNA ratio of GRβ to HSP90 compared with asthma or Bun group. Moreover, there was a significant correlation between GRα and GRβ in protein level, or between GRα and HSP90 both in protein and in mRNA levels. EL may effectively enhance the sensitivity of asthmatic rats to Bun via balancing GR/HSP90. And these findings will be beneficial for the treatment of asthma in the future.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combined Extracts of Epimedii Folium and Ligustri Lucidi Fructus with Budesonide Attenuate Airway Remodeling in the Asthmatic Rats by Regulating Apoptosis and Autophagy.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Aug 5;2020:2319409. doi: 10.1155/2020/2319409. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32831860 Free PMC article.
-
[Experimental study on effect of combination of Epimedii Folium/ Ligustri Lucidi Fructus and dexamethasone on asthmatic rats].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2012 May;37(10):1497-9. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22860470 Chinese.
-
Effects of the combined Herba Epimedii and Fructus Ligustri Lucidi on bone turnover and TGF-β1/Smads pathway in GIOP rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Apr 6;201:91-99. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.02.033. Epub 2017 Feb 27. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28254481
-
Is there a role for glucocorticoid receptor beta in asthma?Respir Res. 2001;2(1):1-4. doi: 10.1186/rr31. Epub 2000 Dec 18. Respir Res. 2001. PMID: 11686858 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glucocorticoid receptor in human respiratory epithelial cells.Neuroimmunomodulation. 2009;16(5):290-9. doi: 10.1159/000216187. Epub 2009 Jun 29. Neuroimmunomodulation. 2009. PMID: 19571590 Review.
Cited by
-
Combined Extracts of Epimedii Folium and Ligustri Lucidi Fructus with Budesonide Attenuate Airway Remodeling in the Asthmatic Rats by Regulating Apoptosis and Autophagy.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Aug 5;2020:2319409. doi: 10.1155/2020/2319409. eCollection 2020. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020. PMID: 32831860 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zöllner E. W., Lombard C., Galal U., Hough S., Irusen E., Weinberg E. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis suppression in asthmatic children on inhaled and nasal corticosteroids - more common than expected? Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2011;24(7-8):529–534. doi: 10.1515/JPEM.2011.198. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

