Inhibitory effect of Gastrodia elata Blume extract on alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone-induced melanogenesis in murine B16F10 melanoma
- PMID: 28584573
- PMCID: PMC5449373
- DOI: 10.4162/nrp.2017.11.3.173
Inhibitory effect of Gastrodia elata Blume extract on alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone-induced melanogenesis in murine B16F10 melanoma
Abstract
Background/objectives: Gastrodia elata Blume (GEB), a traditional herbal medicine, has been used to treat a wide range of neurological disorders (e.g., paralysis and stroke) and skin problems (e.g., atopic dermatitis and eczema) in oriental medicine. This study was designed to investigate whether GEB extract inhibits melanogenesis activity in murine B16F10 melanoma.
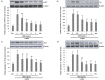
Materials/method: Murine B16F10 cells were treated with 0-5 mg/mL of GEB extract or 400 µg/mL arbutin (a positive control) for 72 h after treatment with/without 200 nM alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone (α-MSH) for 24 h. Melanin concentration, tyrosinase activity, mRNA levels, and protein expression of microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF), tyrosinase, tyrosinase-related protein (Trp)1, and Trp2 were analyzed in α-MSH-untreated and α-MSH-treated B16F10 cells.
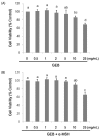
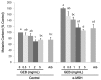
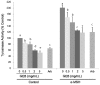
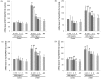
Results: Treatment with 200 nM α-MSH induced almost 2-fold melanin synthesis and tyrosinase activity along with increased mRNA levels and protein expression of MITF, tyrosinase, Trp1 and Trp2. Irrespective of α-MSH stimulation, GEB extract at doses of 0.5-5 mg/mL inhibited all these markers for skin whitening in a dose-dependent manner. While lower doses (0.5-1 mg/mL) of GEB extract generally had a tendency to decrease melanogenesis, tyrosinase activity, and mRNA levels and protein expression of MITF, tyrosinase, Trp1, and Trp2, higher doses (2-5 mg/mL) significantly inhibited all these markers in α-MSH-treated B16F10 cells in a dose-dependent manner. These inhibitory effects of the GEB extract at higher concentrations were similar to those of 400 µg/mL arbutin, a well-known depigmenting agent.
Conclusions: These results suggest that GEB displays dose-dependent inhibition of melanin synthesis through the suppression of tyrosinase activity as well as molecular levels of MITF, tyrosinase, Trp1, and Trp2 in murine B16F10 melanoma. Therefore, GEB may be an effective and natural skin-whitening agent for application in the cosmetic industry.
Keywords: Gastrodia elata; melanogenesis; tyrosinase.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: The authors declare no potential conflicts of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Chang T. Natural melanogenesis inhibitors acting through the down-regulation of tyrosinase activity. c. 2012;5:1661–1685.
-
- Arndt KA, Fitzpatrick TB. Topical use of hydroquinone as a depigmenting agent. JAMA. 1965;194:965–967. - PubMed
-
- Heilgemeir GP, Balda BR. Irreversible toxic depigmentation. Observations following use of hydroquinonemonobenzylether-containing skin bleaching preparations. MMW Munch Med Wochenschr. 1981;123:47–48. - PubMed
-
- Mishima Y, Hatta S, Ohyama Y, Inazu M. Induction of melanogenesis suppression: cellular pharmacology and mode of differential action. Pigment Cell Res. 1988;1:367–374. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

