Injectable hydrogels for cartilage and bone tissue engineering
- PMID: 28584674
- PMCID: PMC5448314
- DOI: 10.1038/boneres.2017.14
Injectable hydrogels for cartilage and bone tissue engineering
Abstract
Tissue engineering has become a promising strategy for repairing damaged cartilage and bone tissue. Among the scaffolds for tissue-engineering applications, injectable hydrogels have demonstrated great potential for use as three-dimensional cell culture scaffolds in cartilage and bone tissue engineering, owing to their high water content, similarity to the natural extracellular matrix (ECM), porous framework for cell transplantation and proliferation, minimal invasive properties, and ability to match irregular defects. In this review, we describe the selection of appropriate biomaterials and fabrication methods to prepare novel injectable hydrogels for cartilage and bone tissue engineering. In addition, the biology of cartilage and the bony ECM is also summarized. Finally, future perspectives for injectable hydrogels in cartilage and bone tissue engineering are discussed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



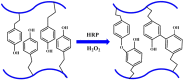
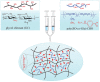
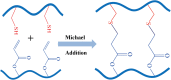


References
-
- Walker KJ, Madihally SV. Anisotropic temperature sensitive chitosan-based injectable hydrogels mimicking cartilage matrix. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 2015; 103: 1149–1160. - PubMed
-
- Söntjens SHM, Nettles DL, Carnahan MA et al. Biodendrimer-based hydrogel scaffolds for cartilage tissue repair. Biomacromolecules 2006; 7: 310–316. - PubMed
-
- Ren K, He C, Xiao C et al. Injectable glycopolypeptide hydrogels as biomimetic scaffolds for cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2015; 51: 238–249. - PubMed
-
- Cancedda R, Dozin B, Giannoni P et al. Tissue engineering and cell therapy of cartilage and bone. Matrix Biol 2003; 22: 81–91. - PubMed
-
- Hjelle K, Solheim E, Strand T et al. Articular cartilage defects in 1,000 knee arthroscopies. Arthroscopy 2002; 18: 730–734. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

