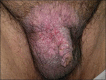
SkIndia Quiz 37: A Persistent Plaque in the Pubic Region
- PMID: 28584770
- PMCID: PMC5447353
- DOI: 10.4103/2229-5178.202362
SkIndia Quiz 37: A Persistent Plaque in the Pubic Region
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
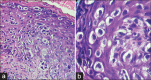
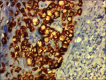
Figures

Similar articles
-
SkIndia Quiz 33: Solitary pigmented plaque containing a blue-gray papule.Indian Dermatol Online J. 2017 Jan-Feb;8(1):70-72. doi: 10.4103/2229-5178.193928. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2017. PMID: 28217486 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
SkIndia Quiz 31: Erythematous plaque over the chin.Indian Dermatol Online J. 2016 Nov-Dec;7(6):558-560. doi: 10.4103/2229-5178.190561. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2016. PMID: 27990407 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
SkIndia Quiz 7: Giant erythematous plaque on the arm of an elderly woman.Indian Dermatol Online J. 2012 Sep;3(3):228-9. doi: 10.4103/2229-5178.96771. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2012. PMID: 23189267 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
[Infectious Inflammation of Pubic Symphysis (Symphysitis Pubis Purulenta): Five Case Reports and Literature View].Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2016;83(6):411-417. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2016. PMID: 28026738 Review. Czech.
-
Locked pubic symphysis into the obturator foramen: a rare case presentation and literature review.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2013 Feb;99(1):106-10. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2012.08.008. Epub 2012 Dec 25. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2013. PMID: 23270720 Review.
References
-
- Rao VR, Henry DH. Extramammary Paget's disease. Commun Oncol. 2004;1:109–14.
-
- Reddy IS, Swain M, Gowrishankar S, Murthy DB. Primary extramammary Paget's disease with extensive skeletal metastases. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2012;78:89–92. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

