Intracardiac metastasis of squamous cell carcinoma of the penis
- PMID: 28584803
- PMCID: PMC5453657
- DOI: 10.4322/acr.2013.035
Intracardiac metastasis of squamous cell carcinoma of the penis
Abstract
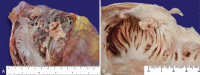
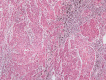
Penile cancer shows variable incidence in different countries with a higher prevalence in developing countries. Squamous cell carcinoma represents the most common histologic type. The seventh decade of life corresponds to the mean age at diagnosis, but it is not an unusual diagnosis among young adults. Most cases present as "in situ" neoplasia or loco regional disease; however, systemic disseminated disease occurs via lymphatic and/or hematogeneous routes. The lymph nodes, liver, and lungs are the most frequently involved sites whereas the heart constitutes an exceptional and atypical site for penile cancer metastases. We report a case of a 79-year-old patient who presented a metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the penis with intracardiac dissemination. The patient had a past history of cardiomyopathy, which required an artificial cardiac pacemaker implantation. He had been treated 1 year before with a partial penectomy but was admitted for emasculation due to the cancer relapse. During the postoperative period, he experienced sudden respiratory distress and died. The autopsy findings showed metastatic disease into the cardiac right chambers, pulmonary tumoral thrombi, and pulmonary hilar involvement. The authors call attention to the possibility of the presence of pacing leads, cardiomyopathy and the altered low blood flow in the right chambers, as predisposing factors for the tumoral seeding in this case.
Keywords: Autopsy; Neoplasm Metastasis; Penile Neoplasms.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Positive lymphoscintigraphy (ILS) and negative computed tomography for metastatic penile cancer.Hell J Nucl Med. 2011 Sep-Dec;14(3):309-10. Hell J Nucl Med. 2011. PMID: 22087456
-
Autopsy findings in 14 patients with penile squamous cell carcinoma.Int J Surg Pathol. 2011 Apr;19(2):164-9. doi: 10.1177/1066896909333781. Epub 2009 May 1. Int J Surg Pathol. 2011. PMID: 19411278
-
Comparison of morphologic features and outcome of resected recurrent and nonrecurrent squamous cell carcinoma of the penis: a study of 81 cases.Am J Surg Pathol. 2009 Sep;33(9):1299-306. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181a418ae. Am J Surg Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19471153
-
[A Case of Autopsy of Sarcomatoid Carcinoma of the Penis with Metastasis to the Right Ventricle of the Heart].Hinyokika Kiyo. 2018 Nov;64(11):455-458. doi: 10.14989/ActaUrolJap_64_11_455. Hinyokika Kiyo. 2018. PMID: 30543746 Review. Japanese.
-
Metastasis to the penis in a patient with squamous cell carcinoma of the lung with a review of reported cases.Lung Cancer. 2001 Oct;34(1):149-52. doi: 10.1016/s0169-5002(01)00226-4. Lung Cancer. 2001. PMID: 11557125 Review.
Cited by
-
Left Ventricular Metastases from Penile Squamous Cell Carcinoma.CASE (Phila). 2022 Feb 16;6(2):67-72. doi: 10.1016/j.case.2022.01.009. eCollection 2022 Apr. CASE (Phila). 2022. PMID: 35492291 Free PMC article.
-
Novel presentation of intraocular metastases in a patient with penile squamous cell carcinoma: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2020 Oct 23;14(1):199. doi: 10.1186/s13256-020-02520-8. J Med Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 33092626 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arya M, Kalsi J, Kelly J, Muneer A. Malignant and premalignant lesions of the penis. BMJ. 2013;346:f1149 http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.f1149. - DOI - PubMed
-
- European Association of Urology. Online guidelines [Internet]. [place unknown]: European Association of Urology; 2012. Available from: www.uroweb.org/guidelines/online-guidelines/
-
- American Cancer Society. What are key statistics about penile cancer? [place unknown]; c2013 [cited 2013 May 29]. Available from: http://www.cancer.org/cancer/penilecancer/detailedguide/penile-cancer-ke...
-
- Favorito LA, Nardi AC, Ronalsa M, Zequi SC, Sampaio FJ, Glina S. Epidemiologic study on penile cancer in Brazil. Int Braz J Urol. 2008;34:587-91. http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1677-55382008000500007. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ebele JN, Sauter G, Epstein JI, Sesterhenn IA. Pathology and genetics of tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs. Lyon: IARC Press; 2004.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

