A Subset of Extreme Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Controllers Is Characterized by a Small HIV Blood Reservoir and a Weak T-Cell Activation Level
- PMID: 28584850
- PMCID: PMC5450900
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofx064
A Subset of Extreme Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Controllers Is Characterized by a Small HIV Blood Reservoir and a Weak T-Cell Activation Level
Abstract
Background: Human immunodeficiency virus controllers (HICs) form a heterogeneous group of patients with regard to formal definitions, immunologic characteristics, and changes over time in viral load.
Patients and methods: The HICs with undetectable viral load ([uHICs] ie, for whom a viral load had never been detected with routine assays; n = 52) were compared with 178 HICs with blips during the follow up (bHICs). Clinical characteristics, ultrasensitive HIV-ribonucleic acid (RNA) and HIV-deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) loads, HIV1-Western blot profiles, and immune parameters were analyzed.
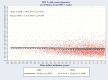
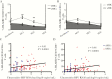
Results: Relative to bHICs, uHICs had significantly lower ultrasensitive plasma HIV-RNA loads (P < .0001) and HIV-DNA levels in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (P = .0004), higher CD4+ T-cell count (P = .04) at enrollment, and lower T-cell activation levels. Between diagnosis and inclusion in the cohort, the CD4+ T-cell count had not changed in uHICs but had significantly decreased in bHICs. Twenty-one percent of the uHICs lacked specific anti-HIV immunoglobulin G antibodies, and these individuals also had very low levels of HIV-DNA. Half of the uHICs had a protective human leukocyte antigen (HLA) allele (-B57/58/B27), a weak CD8+ T-cell response, and very small HIV-DNA reservoir.
Conclusions: We suggest that an interesting HIC phenotype combines protective HLA alleles, low level of HIV blood reservoirs, and reduced immune activation. Prospective studies aimed at evaluating the benefit of combined antiretroviral therapy in HICs might take into account the identification of uHICs and bHICs.
Keywords: HIV controllers; HIV-DNA in PBMC; HLA; immune activation; ultrasensitive plasma HIV-RNA load..
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures

References
-
- Okulicz JF, Lambotte O. Epidemiology and clinical characteristics of elite controllers. Curr Opin HIV AIDS 2011; 6:163–8. - PubMed
-
- Lambotte O, Boufassa F, Madec Y, et al. HIV controllers: a homogeneous group of HIV-1-infected patients with spontaneous control of viral replication. Clin Infect Dis 2005; 41:1053–6. - PubMed
-
- Walker BD. Elite control of HIV Infection: implications for vaccines and treatment. Top HIV Med 2007; 15:134–6. - PubMed
-
- Lamine A, Caumont-Sarcos A, Chaix ML, et al. Replication-competent HIV strains infect HIV controllers despite undetectable viremia (ANRS EP36 study). AIDS 2007; 21:1043–5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

