4β-Hydroxycholesterol level significantly correlates with steady-state serum concentration of the CYP3A4 substrate quetiapine in psychiatric patients
- PMID: 28585378
- PMCID: PMC5651320
- DOI: 10.1111/bcp.13341
4β-Hydroxycholesterol level significantly correlates with steady-state serum concentration of the CYP3A4 substrate quetiapine in psychiatric patients
Abstract
Aim: 4β-Hydroxycholesterol (4βOHC) is sensitive towards induction or inhibition of CYP3A4, but its potential usefulness as a dosing biomarker remains to be demonstrated. The aim of this study was to investigate the correlation between 4βOHC levels and steady-state concentrations (Css) of quetiapine, a CYP3A4 substrate with high presystemic metabolism, in psychiatric patients.
Methods: Serum samples from 151 patients treated with quetiapine as immediate release (IR; n = 98) or slow release (XR; n = 53) tablets were included for analysis of 4βOHC. In all patients, Css of quetiapine had been measured at trough level, i.e. 10-14 and 17-25 h post-dosing for IR and XR tablets, respectively. Correlations between 4βOHC levels and dose-adjusted Css (C/D ratios) of quetiapine were tested by univariate (Spearman's) and multivariate (multiple linear regression) analyses. Gender, age (≥60 vs. <60 years) and tablet formulation were included as potential covariates in the multivariate analysis.
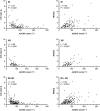
Results: Correlations between 4βOHC levels and quetiapine C/D ratios were highly significant both for IR- and XR-treated patients (P < 0.0001). Estimated Spearman r values were -0.47 (95% confidence interval -0.62, -0.30) and -0.56 (-0.72, -0.33), respectively. The relationship between 4βOHC level and quetiapine C/D ratio was also significant in the multiple linear regression analysis (P < 0.001), including gender (P = 0.023) and age (P = 0.003) as significant covariates.
Conclusions: The present study shows that 4βOHC level is significantly correlated with steady-state concentration of quetiapine. This supports the potential usefulness of 4βOHC as a phenotype biomarker for individualized dosing of quetiapine and other drugs where systemic exposure is mainly determined by CYP3A4 metabolism.
Keywords: 4β-hydroxycholesterol; CYP3A4; biomarker; quetiapine.
© 2017 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures

Comment in
-
Was 4β-hydroxycholesterol ever going to be a useful marker of CYP3A4 activity?Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2018 Jul;84(7):1620-1621. doi: 10.1111/bcp.13538. Epub 2018 Feb 21. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29464732 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Gjestad et al. reply to 'Was 4β-hydroxycholesterol ever going to be a useful marker of CYP3A4 activity?' by Neuhoff and Tucker.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2018 Jul;84(7):1624-1625. doi: 10.1111/bcp.13606. Epub 2018 May 10. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29749106 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Zanger UM, Schwab M. Cytochrome P450 enzymes in drug metabolism: regulation of gene expression, enzyme activities, and impact of genetic variation. Pharmacol Ther 2013; 138: 103–141. - PubMed
-
- Lin YS, Lockwood GF, Graham MA, Brian WR, Loi CM, Dobrinska MR, et al. In‐vivo phenotyping for CYP3A by a single‐point determination of midazolam plasma concentration. Pharmacogenetics 2001; 11: 781–791. - PubMed
-
- Hole K, Gjestad C, Heitmann KM, Haslemo T, Molden E, Bremer S. Impact of genetic and nongenetic factors on interindividual variability in 4beta‐hydroxycholesterol concentration. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 2017; 73: 317–324. - PubMed
-
- Fuhr U, Jetter A, Kirchheiner J. Appropriate phenotyping procedures for drug metabolizing enzymes and transporters in humans and their simultaneous use in the ‘cocktail’ approach. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2007; 81: 270–283. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

