Design, synthesis and evaluation of novel cinnamic acid derivatives bearing N-benzyl pyridinium moiety as multifunctional cholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 28585866
- PMCID: PMC6009898
- DOI: 10.1080/14756366.2016.1256883
Design, synthesis and evaluation of novel cinnamic acid derivatives bearing N-benzyl pyridinium moiety as multifunctional cholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
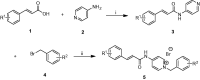
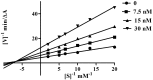
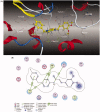
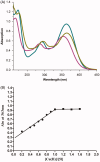
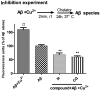
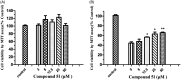
A novel family of cinnamic acid derivatives has been developed to be multifunctional cholinesterase inhibitors against AD by fusing N-benzyl pyridinium moiety and different substituted cinnamic acids. In vitro studies showed that most compounds were endowed with a noteworthy ability to inhibit cholinesterase, self-induced Aβ (1-42) aggregation, and to chelate metal ions. Especially, compound 5l showed potent cholinesterase inhibitory activity (IC50, 12.1 nM for eeAChE, 8.6 nM for hAChE, 2.6 μM for eqBuChE and 4.4 μM for hBuChE) and the highest selectivity toward AChE over BuChE. It also showed good inhibition of Aβ (1-42) aggregation (64.7% at 20 μM) and good neuroprotection on PC12 cells against amyloid-induced cell toxicity. Finally, compound 5l could penetrate the BBB, as forecasted by the PAMPA-BBB assay and proved in OF1 mice by ex vivo experiments. Overall, compound 5l seems to be a promising lead compound for the treatment of Alzheimer's diseases.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; benzylpyridinium; cinnamic acid; metal chelator; neuroprotection; β-amyloid aggregation.
Figures

References
-
- Thies W, Bleiler L.. Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimer's Dement 2013;9:208–45. - PubMed
-
- Tang H, Zhao HT, Zhong SM, et al. . Novel oxoisoaporphine-based inhibitors of acetyl- and butyrylcholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase-induced beta-amyloid aggregation. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2012;22:2257–61. - PubMed
-
- Laferla FM, Green KN, Oddo S. Intracellular amyloid-beta in Alzheimer's disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 2007;8:499–509. - PubMed
-
- Wilkinson D, Wirth Y, Goebel C.. Memantine in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease: meta-analyses using realistic definitions of response. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 2014;37:71–85. - PubMed
-
- Xie Q, Wang H, Xia Z, et al. . Bis-(-)-nor-meptazinols as novel nanomolar cholinesterase inhibitors with high inhibitory potency on amyloid-beta aggregation. J Med Chem 2008;51:2027–36. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
