MERS-CoV Antibody Responses 1 Year after Symptom Onset, South Korea, 2015
- PMID: 28585916
- PMCID: PMC5512479
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2307.170310
MERS-CoV Antibody Responses 1 Year after Symptom Onset, South Korea, 2015
Abstract
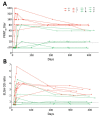
We investigated the kinetics of the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) neutralizing and spike protein antibody titers over the course of 1 year in 11 patients who were confirmed by reverse transcription PCR to have been infected during the outbreak in South Korea in 2015. Robust antibody responses were detected in all survivors who had severe disease; responses remained detectable, albeit with some waning, for <1 year. The duration of viral RNA detection (but not viral load) in sputum significantly correlated with the antibody response magnitude. The MERS S1 ELISA antibody titers correlated well with the neutralizing antibody response. Antibody titers in 4 of 6 patients who had mild illness were undetectable even though most had evidence of pneumonia. This finding implies that MERS-CoV seroepidemiologic studies markedly underestimate the extent of mild and asymptomatic infection. Obtaining convalescent-phase plasma with high antibody titers to treat MERS will be challenging.
Keywords: China; MERS; MERS-CoV; Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus; South Korea; antibody; coronavirus; human; kinetics; neutralization; serology; viruses; zoonoses.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO MERS-CoV global summary and risk assessment. 2016 Dec 5 [cited 2017 Jan 21]. http://www.who.int/emergencies/mers-cov/mers-summary-2016.pdf?ua=1
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

