Stabilization of lead in incineration fly ash by moderate thermal treatment with sodium hydroxide addition
- PMID: 28586368
- PMCID: PMC5460817
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0178816
Stabilization of lead in incineration fly ash by moderate thermal treatment with sodium hydroxide addition
Abstract
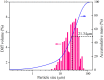
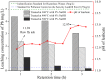
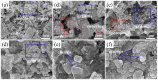
Municipal solid waste (MSW) incineration fly ash (IFA) can be potentially reused as a substitute for some raw materials, but treatment for detoxification is indispensable owing to high contents of heavy metals in fly ash. In the present work, due to excessive leaching concentration of lead (Pb), a moderate thermal treatment with sodium hydroxide (NaOH) addition was employed to stabilize Pb in IFA. The moderate thermal treatment was performed under relatively low temperature ranging from 300 to 500°C and at retention time from 1 to 3 h with NaOH addition in a range of 1 to 9%. Leaching results showed that leaching concentrations of Pb in IFA leachates decreased below the standard for hazardous waste identification (5 mg/L) in China under all treatment scenarios. With the increase of temperature, retention time and the amount of NaOH, the concentration of Pb were further suppressed in IFA leachates. Especially, at 500°C for 3 h with 9% NaOH addition, the concentration of Pb dropped to 0.18 mg/L, which was below the standard for sanitary landfill (0.25 mg/L) in China. In thermal process, needle-like crystallites melted to form granules and clumps with compacter structure and less pores. After the thermal treatment, water-soluble and exchangeable fractions of Pb significantly decreased. Therefore, the thermal treatment coupled with NaOH could be applied to realize the environmentally sound management of MSW IFA.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
A novel and sustainable technique to immobilize lead and zinc in MSW incineration fly ash by using pozzolanic bottom ash.J Environ Manage. 2023 Mar 1;329:117036. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.117036. Epub 2022 Dec 17. J Environ Manage. 2023. PMID: 36535140
-
Resource recovery from MSW incineration residues through the 'Ash-by-Ash Treatment Method' (AATM): optimization of water and bottom ash contents.Environ Technol. 2025 Aug;46(19):3804-3821. doi: 10.1080/09593330.2025.2478179. Epub 2025 Mar 19. Environ Technol. 2025. PMID: 40106721
-
Influence of flue gas SO2 on the toxicity of heavy metals in municipal solid waste incinerator fly ash after accelerated carbonation stabilization.J Hazard Mater. 2011 Sep 15;192(3):1609-15. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.06.085. Epub 2011 Jul 5. J Hazard Mater. 2011. PMID: 21782326
-
Municipal solid waste (MSW) incineration fly ash as an important source of heavy metal pollution in China.Environ Pollut. 2019 Sep;252(Pt A):461-475. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.04.082. Epub 2019 Apr 17. Environ Pollut. 2019. PMID: 31158674 Review.
-
Chemical stabilization of heavy metals in municipal solid waste incineration fly ash: a review.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022 Jun;29(27):40384-40402. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-19649-2. Epub 2022 Mar 26. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35338465 Review.
References
-
- Jin Y, Ma X, Jiang X, Liu H, Li X, Yan J, et al. Effects of hydrothermal treatment on the major heavy metals in fly ash from municipal solid waste incineration. Energy Fuels. 2012; 27(1): 394–400.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

